Table of Contents
Enable UART Serial Communication
Edit /boot/config.txt and append:
enable_uart=1
to the end of the file and reboot.
Disable Wifi Power Management
When receiving large amounts of output over SSH the Raspberry Pi might render the console inoperable and the connection will time out in a few seconds.
The following command adds some module options to the wifi kernel module to disable power management which is apparently responsible for the former issue.
echo "options 8192cu rtw_power_mgnt=0 rtw_enusbss=0" | sudo tee --append /etc/modprobe.d/8192cu.conf
Enable SSH on (First) Boot
Create a blank file named ssh with no extension at the root of the boot partition of the SD card in order to make Raspbian start the SSH daemon on boot. One use for this trick is combining the Raspberry Pi with an ethernet hat such that the Raspberry can be setup without needing to attach a monitor and keyboard.
Check if Hardware Decoders are Enabled
vcgencmd codec_enabled MPG2 vcgencmd codec_enabled WVC1
Note that the Raspberry Pi 4 does not have hardware decoders such that the commands will most likely state disabled.
Change Audio Output
Issuing:
amixer controls
will yield the controls available on the Raspberry Pi:
# amixer controls numid=3,iface=MIXER,name='PCM Playback Route' numid=2,iface=MIXER,name='PCM Playback Switch' numid=1,iface=MIXER,name='PCM Playback Volume'
The Raspberry Pi 2,3 and 4 can commute between sending sound through the  audio jack:
audio jack:
amixer cset numid=3 1
or the HDMI output:
amixer cset numid=3 2
respectively, or:
amixer cset numid=3
to set the sound selection to autodetect where the jack will be used only if the HDMI cable is not connected.
Logging-in via SSH over USB
The Raspberry Pi when connected to a PC can configure itself as an USB gadget and start a network over USB. A RNDIS network adapter is needed in most cases and can be downloaded from here:
In order to log into the Raspberry Pi over SSH via the USB port, edit config.txt and add:
dtoverlay=dwc2,dr_mode=peripherial
and also, make sure to comment out otg_mode=1 because it will be handled by dwc2.
Next, edit cmdline.txt and add the following to the kernel parameters between rootwait and quiet:
modules-load=dwc2,g_ether
Finally, add a blank file named ssh with no contents to the root of the boot partition.
The Raspberry can now be connected to a PC via its USB port (not the USB port marked PWR). The PC that the Raspberry Pi connects to will act as a router and should forward packets to the Raspberry Pi.
When the RNDIS interface is brought up, if Apple bonjour is installed and running on the machine that the Raspberry Pi is connected to, then the Raspberry Pi is supposed to register the DNS address raspberry.local via mDNS with Windows. Even if Apple bonjour is installed, the name might not be assigned even though the Rasbperry Pi might be configured properly as per the above. Also, it seems that in some cases when the RNDIS interface is brought up, the Raspberry Pi does not send any packets as all making an ARP table query via arp -a entirely futile.
The first attempt would be to try connecting via the assigned DNS address: ssh pi@raspberry.local and enter raspberry at the password prompt. if that fails, a packet sniffer such as WireShark or TcpDump may reveal the initial Raspberry Pi's ARP requests for Google's DNS servers (8.8.8.8). Sometimes just restarting the bonjour service and disabling and re-enabling the RNDIS interface may get the Raspberry Pi to register its name.
Connecting to a Bridge Automatically
In order to connect the Raspberry Pi to a bridge as it is connected to a server, an udev rule can be written that will match all RNDIS adapters and connect them to a bridge.
The only changes required on the Raspberry Pi is to edit /etc/network/interfaces.d/usb0 and add the lines:
auto usb0 iface usb0 inet dhcp
and save the file. This will make sure that when the Raspberry Pi boots, an IP address will be requested over the usb0 interface and will work provided that the computer that the Raspberry Pi is connected to is running a DHCP server on the other end.
Restoring for Normal USB Operation
After configuring, the USB port makes the Raspberry Pi act like a gadget device and in order to connect regular USB hardware, the configuration has to be altered. Edit /boot/cmdline.txt and /boot/config.txt to remove the previous changes and reboot. Devices should connect normally now and should be recognized.
Enabling Monitor Mode via Nexmon Drivers
Some Raspberry Pi devices such as the Raspberry Pi Zero W can operate in monitor mode in order to sniff wireless traffic. Up to this date, there is no official way to get monitor mode working for the Raspberry SoC except for using alternative Nexmon drivers that replace the brcmfmac kernel module with a patched module enabling monitor mode. Unfortunately, the Nexmon drivers lag behind and last successful builds are known to work with Raspbian Jessie at best.
Here is a short guide on how to build the nexmon drivers for Raspberry Pi W and substitute the kernel module in order to enable monitor mode.
Install required packages to compile the drivers:
apt-get install subversion raspberrypi-kernel-headers git libgmp3-dev gawk qpdf bison flex make autoconf automake build-essential libtool libisl10
Change directory to a compile space:
cd /usr/src
and check out the source (official):
git clone https://github.com/MaximusBaton/nexmon.git
or from Wizardry and Steamworks:
svn co http://svn.grimore.org/nexmon
Set variables:
export NEXMON_ROOT=/usr/src/nexmon
and load the provided environment:
source setup_env.sh
Now compile the nexmon package from the top-level:
make
Now build the kernel module and firmware:
cd patches/bcm43430a1/7_45_41_46/nexmon/
where:
bcm43430a1is for the Raspberry Pi Zero W
make
Now generate a backup of the original firmware file and install the patched firmware:
make backup-firmware make install-firmware
Compile nexutil since it might come in handy:
cd utilities/nexutil make install
Now to make the Raspberry load the modified kernel module after reboot it, the existing module is simply substituted for the module that was compiled at the previous step:
PATH_OF_DEFAULT_DRIVER_AT_REBOOT=$(modinfo brcmfmac | grep -m 1 -oP "^filename:(\s*?)(.*)$" | sed -e 's/^filename:\(\s*\)\(.*\)$/\2/g') mv "$PATH_OF_DEFAULT_DRIVER_AT_REBOOT" "$PATH_OF_DEFAULT_DRIVER_AT_REBOOT.orig" cp patches/bcm43430a1/7_45_41_46/nexmon/brcmfmac_4.14.y-nexmon/brcmfmac.ko $PATH_OF_DEFAULT_DRIVER_AT_REBOOT
Finally, generate module dependencies:
depmod -a
In order to set up the Wifi monitoring interface on boot, create the file /etc/network/interfaces.d/mon0 with the following contents:
auto mon0 iface mon0 inet manual pre-up iw wlan0 interface add mon0 type monitor wireless-mode monitor
and restart the Raspberry Pi.
Running a One-Off Script on First Machine Boot
To execute a script unconditionally edit /boot/cmdline.txt and set init to mount virtual filesystems and then execute a script. For example, the /boot/cmdline.txt file would contain:
init=/bin/bash -- -c "mount -t proc proc /proc; mount -t sysfs sys /sys; mount /boot; source /boot/firstboot.sh"
that will end up executing /boot/firstboot.sh.
The contents of /boot/firstboot.sh should make sure to remove the init parameter from the kernel command line such that the first boot script does not run again, then perform the necessary operations and finally restart the system:
# Boot mount -t tmpfs tmp /run mkdir -p /run/systemd mount / -o remount,rw # Ensure the script does not run again. sed -i 's| init=.*||' /boot/cmdline.txt # Run # Insert custom commands. /usr/lib/raspi-config/init_resize.sh /usr/bin/ssh-keygen -A # Reboot sync umount /boot mount / -o remount,ro sync echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger sleep 5
Downgrade or Upgrade to Specific Kernel Version
Pick a commit from the rpi-firmware github project, look at the commit hash and then issue:
rpi-update HASH
where:
HASH- is the commit hash
Downgrade to Last Stable Firmware
apt-get install --reinstall raspberrypi-bootloader raspberrypi-kernel
Fixing a Blinking Monitor
Some HDMI-to-VGA adapters that do not have their own power source draw more power from the Raspberry Pi such that sometimes the signal provided by the Raspberry Pi is insufficient. Fortunately the Raspberry Pi firmware allows to boost the signal by editing the file /boot/config.txt on the boot partition. Open /boot/config.txt and uncomment the line reading config_hdmi_boost and gradually increase the value until the blinking of the monitor is gone.
Simultaneously Playing Audio through Headphones (analog) and HDMI (digital)
Create a file at either ~/.asoundrc or at /etc/asound.conf in order to play audio through both the headphone jack and the first HDMI port.
###########################################################################
## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2021 - License: GNU GPLv3 ##
###########################################################################
# Plays audio simultaneously through HDMI 0 an the Headphones jack on RPi #
# #
# To use, place this file where ALSA picks up configuration files. #
# Usually at ~/.asoundrc or /etc/asound.conf #
###########################################################################
pcm.both {
type route;
slave.pcm {
type multi
slaves.a.pcm "hdmi:CARD=vc4hdmi0,DEV=0"
slaves.a.channels 2
slaves.b.pcm "hw:CARD=Headphones"
slaves.b.channels 2
bindings.0.slave a
bindings.0.channel 0
bindings.1.slave a
bindings.1.channel 1
bindings.2.slave b
bindings.2.channel 0
bindings.3.slave b
bindings.3.channel 1
}
ttable.0.0 1
ttable.1.1 1
ttable.0.2 1
ttable.1.3 1
}
ctl.both {
type hw
card Headphones
}
pcm.stereo {
type route
slave.pcm "both"
ttable.0.0 1
ttable.1.1 1
ttable.0.2 1
ttable.1.3 1
}
pcm.!default {
type plug
slave {
pcm stereo
}
}
ctl.!default {
type hw
card Headphones
}
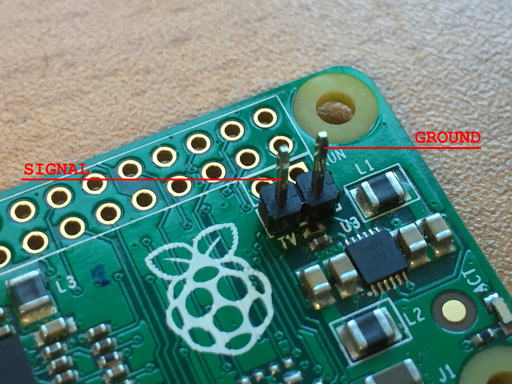
Getting Composite Video Output via RCA Jack on Raspberry Pi Zero
The Raspberry Pi Zero can output composite video by connecting to the two pins adjacent to the main pin header.
where, the right-most pin is ground and the left-most pin is the video signal.
After making the necessary connections, edit /boot/config.txt on the Raspberry Pi and:
- disable the forced HDMI output, by commenting out
hdmi_force_hotplug=1, - enable
sdtv_mode=2
After a reboot, the Raspbery Pi Zero should output composite video on the pins.
On newer distributions such as bookworm, the parameters have changed. Fist, edit /boot/config.txt and disable HDMI and enable composite:
# Enable DRM VC4 V3D driver (this line already exists so change it) dtoverlay=vc4-kms-v3d,composite hdmi_ignore_hotplug=1 hdmi_ignore_cec_init=1 enable_tvout=1
and then change /boot/cmdline.txt to set a video resolution and standard by appending the following:
video=Composite-1:720x480@60ie
After a restart, the Raspberry Pi should boot up and send a composite signal instead of sending video through HDMI.
Disable LED on Rasperry Pi Zero W 2
Insert into /boot/firmware/config.txt, the following lines:
dtparam=act_led_trigger=none dtparam=act_led_activelow=on
and reboot.
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.