Table of Contents
Find Longest Line in a File
awk ' { if ( length > x ) { x = length } }END{ print x }' file.txt
Perform Floating Point Calculations
awk can be used for complex calculations, for example:
awk 'BEGIN {printf "%.3f\n", sin(30 * atan2(0, -1)/180)}'
will calculate 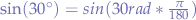 and return:
and return:
0.500
Since awk does not have a constant for  , we use
, we use atan2(0, -1) instead.
Delimiter-Style
Suppose you have a file input containing data separated by delimiters such as:
variable = value
or:
variable = value
The following command can be used to obtain value:
awk -F"[ \t]*[=][ \t]*" '{ print $2 }' input
Remove Duplicate Entries in File Without Sorting
To remove all duplicates from file.txt without sorting, issue:
awk '!x[$0]++' file.txt
Merge Lines by Two in File
Given a file with the contents:
Q: What is this? A: This is a FAQ!
and you would like to achieve:
Q: What is this? A: This is a FAQ!
then the following awk one liner:
awk 'NR%2{printf "%s ",$0;next;}1' yourFile
will merge all the lines in a file by two.
Convert Key-Value Map to JSON
Given an input such as:
a1 : "abc c2 : def e3 : "ghi " f5 :" a b"
The following awk script:
awk -F: ' function trim(s) { return gensub(/^[ \t"]*|[ \t"]*$/, "", "g", s) } BEGIN { printf "{" } NR > 1 { printf(", ") } { printf("\"%s\":\"%s\"", trim($1), trim(substr($0, index($0,":") + 1))); } END { print "}" } '
will return the JSON object:
{"a1":"abc","c2":"def","e3":"ghi","f5":"a b"}
where keys and values are trimmed for spaces and quotes from the start and end.
One example application would be creating a JSON object out of the status of an APC UPS:
apcaccess | awk -F: ' function trim(s) { return gensub(/^[ \t"]*|[ \t"]*$/, "", "g", s) } BEGIN { printf "{" } NR > 1 { printf(", ") } { printf("\"%s\":\"%s\"", trim($1), trim(substr($0, index($0,":") + 1))); } END { print "}" } '
Netstat with Awk
From qistoph.
# Based on gist https://gist.github.com/staaldraad/4c4c80800ce15b6bef1c1186eaa8da9f # - added TCP states awk 'BEGIN{states["01"]="TCP_ESTABLISHED" states["02"]="TCP_SYN_SENT" states["03"]="TCP_SYN_RECV" states["04"]="TCP_FIN_WAIT1" states["05"]="TCP_FIN_WAIT2" states["06"]="TCP_TIME_WAIT" states["07"]="TCP_CLOSE" states["08"]="TCP_CLOSE_WAIT" states["09"]="TCP_LAST_ACK" states["0A"]="TCP_LISTEN" states["0B"]="TCP_CLOSING" states["0C"]="TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV" } function hextodec(str,ret,n,i,k,c){ ret = 0 n = length(str) for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) { c = tolower(substr(str, i, 1)) k = index("123456789abcdef", c) ret = ret * 16 + k } return ret } function getIP(str,ret){ ret=hextodec(substr(str,index(str,":")-2,2)); for (i=5; i>0; i-=2) { ret = ret"."hextodec(substr(str,i,2)) } ret = ret":"hextodec(substr(str,index(str,":")+1,4)) return ret } NR > 1 {{if(NR==2)print "Local - Remote";local=getIP($2);remote=getIP($3)}{print local" - "remote" "states[$4]}}' /proc/net/tcp
Compute the Standard Deviation of a Column of Numbers
From the very question on how to compute the standard deviation:
awk '{ x += $0; y += $0 ^ 2 } END { print sqrt( y/NR - (x/NR) ^ 2) }'
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.



