Table of Contents
About
A binary tree is a tree data structure where each node has a left and a right child.
Terminology
- A rooted binary tree has a root node and every node has at most two children.
- A full binary tree is a tree where every node has either
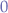 or
or 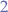 children.
children. - A perfect binary tree is a binary tree where all nodes have two children and all leaves have the same depth.
- A complete binary tree has every level filled except possibly the last and all the nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between
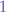 and
and 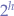 nodes where
nodes where 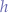 is the height of the tree.
is the height of the tree. - An infinite complete binary tree is a tree where every node has two children and the depth is countably infinite.
- A balanced binary tree is a binary tree where the left and right subtrees of every node differ in height by no more than
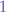 .
. - A degenerate binary tree is a tree where each parent node has only one child node.
Properties
- The number of nodes
 in a full binary tree is at least
in a full binary tree is at least 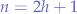 and at most
and at most 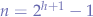 where
where  is the height of the tree. A tree with only a root node has a height of
is the height of the tree. A tree with only a root node has a height of  .
. - The number of leaves
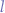 in a perfect binary tree is
in a perfect binary tree is 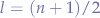 because the number of non-leaf (internal) nodes is
because the number of non-leaf (internal) nodes is 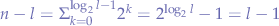 .
. - A perfect binary tree with
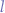 leaves has
leaves has 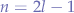 nodes.
nodes.
Representing with Arrays
![Equation $$
\tikzset{
treenode/.style = {align=center, inner sep=0pt, text centered,
font=\sffamily},
arn_n/.style = {treenode, circle, white, font=\sffamily\bfseries, draw=black,
fill=black, text width=1.5em},% arbre rouge noir, noeud noir
arn_r/.style = {treenode, circle, red, draw=red,
text width=1.5em, very thick},% arbre rouge noir, noeud rouge
arn_x/.style = {treenode, rectangle, draw=black,
minimum width=0.5em, minimum height=0.5em}% arbre rouge noir, nil
}
\begin{tikzpicture}[->,>=stealth',level/.style={sibling distance = 2cm/#1,
level distance = 1cm},font=\ttfamily,
array/.style={matrix of nodes,
row sep=1.5mm,
column sep=-\pgflinewidth,
nodes={rectangle,draw=black,minimum size=1mm, fill=orange!30},
%row 1/.style={nodes={fill=orange!30}},
row 6/.style={nodes={fill=green!30}},
%column 1/.style={nodes={fill=white!30}},
text depth=0.05ex,
text height=1ex,
nodes in empty cells}
]
\begin{scope}
\node[arn_r] (48) {48}
child { node[arn_n] (40) {40}
child { node[arn_n] (8) {8} }
child { node[arn_n] (20) {20} } }
child { node[arn_n] (13) {13}
child { node[arn_n] (12) {12} }
child { node[arn_n] (8) {8} } };
\end{scope}
\begin{scope}[yshift=-3.5cm]
\matrix[array] (array) {
\color{red}{48} & 40 & 13 & 8 & 20 & 12 & 8 \\
};
\draw[->,solid, thick, color=red] (array-1-1) to [out=-100,in=-100] node { \fcolorbox{red}{red}{\color{white}\tiny $2i+1$} } (array-1-2);
\draw[->,solid, thick, color=red] (array-1-1) to [out=100,in=100] node { \fcolorbox{red}{red}{\color{white}\tiny $2i+2$} } (array-1-3);
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}
$$](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/imgd6d934db012f507b9066ec1885b3e375.png)
A binary tree can be represented using an array data structure. In case the tree is complete then this method does not waste any space.
The index of the left-node is given by:

The index of the right-node is given by:

The index of the parent of a node is given by:
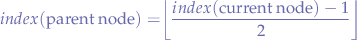
where:
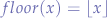 is the largest interger less than or equal to
is the largest interger less than or equal to  .
.
Implementations
Index
fuss/data_structures/trees/binary_trees.txt · Last modified: by 127.0.0.1
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.



