VIC
VIC is a pencil and paper cypher using a straddling checkerboard as well as several other known techniques used to further obfuscate the message.
To encrypt, a straddling checkerboard is set-up by following the rules:
- The first row is numbered from
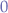 to
to  .
. - The second row is populated with the most frequent letters of the alphabet (
ESTORNIA-R), in no particular order, and by leaving two blanks below two arbitrary numbers from the first row. - The remaining rows are numbered with the numbers from the first row that have a blank in the second row.
- The remaining rows are then filled-in with the rest of the alphabet (in no particular order).
- Any spare cells which can be filled with any non-literal character.
- It does not matter where the spaces and the non-literal characters are placed as long as the receiver uses the same system.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 --------------------- E T A O N R I S --------------------- 4 B C / D F G H J K L --------------------- 6 M P Q U V W X Y Z .
To encrypt, every letter from the checkerboard is mapped to rows and columns (or just columns if it occurs in the second row).
As an example, to encrypt let there be:
L E T T H E R E B E 49 0 1 1 46 0 7 0 40 0
The resulting message 4901146070400 can be sent out directly or processed further through a second cypher stage such as transposition or substitution. As an example, we can add a key 0727 using modular arithmetic:
4901146070400 0727072707270 ------------- (+) 4628118777670
Optionally, the same straddling checkerboard can be used to convert the cypher-text back into letters. Since we have chosen two blanks for 4 and 6, whenever we find those numbers in the first position, we group the numbers together (because 4 and 6 have a blank space in the second row of the checkerboard and cannot be converted to letters):
46 2 8 1 1 8 7 7 7 67 0 ----------------------- H A I T T I R R R Y E
resulting in the cypher-text: HAITTIRRRYE.
In order to decrypt, one must know the chosen structure of the checkerboard and the successive operations used to obtain the cypher-text.
In essence, VIC is a hybrid cypher that combines multiple methods of substitution and transposition in order to obtain the cypher-text. It is a very strong cypher due to the number of operations performed during encryption but that also results in a larger shared secret between the sender and the receiver - ie: the checkerboard structure is arbitrary, the whole thing must be established before messages can be sent; adding a key to the procedure for a further transposition also means that the key must be known and, lastly, the order of operations must be known in order to be able to reverse the cypher.
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.



