Note
The wasBinarySearchTreeInsert function takes as arguments:
- a binary search tree (
BST) as a flattened list as per binary_trees. - the root of the binary search tree (
root) - the node (
node) to insert into the binary search tree.
and returns the resulting binary search tree.
Code

// Ord() function, written by Pedro Oval, 2010-05-28 // Inlined by Wizardry and Steamworks integer Ord(string chr) { if (chr == "") return 0; string hex = llEscapeURL(chr); if (llGetSubString(hex, 0, 0) != "%") return llBase64ToInteger("AAAA" + llStringToBase64(llGetSubString(chr, 0, 0))); integer b = (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 1, 2)); if (b < 194 || b > 244) return b; if (b < 224) return ((b & 0x1F) << 6) | (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 4, 5)) & 0x3F; if (b < 240) return (b & 0x0F) << 12 + ((integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 4, 5)) & 0x3F) << 6 + (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 7, 8)) & 0x3F; return (b & 0x07) << 18 + ((integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 4, 5)) & 0x3F) << 12 + ((integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 7, 8)) & 0x3F) << 6 + (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 10, 11)) & 0x3F; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Copyright (C) 2013 Wizardry and Steamworks - License: GNU GPLv3 // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// integer wasOrdCompare(string chra, string chrb) { // numerical float fa = (float)chra; float fb = (float)chrb; if(fa != 0 && fb != 0) { if(fa > fb) return 1; if(fa < fb) return -1; return 0; } // lexical if(llStringLength(chra) == 0 && llStringLength(chrb) == 0) return 0; if(llStringLength(chra) && llStringLength(chrb) == 0) return 1; if(llStringLength(chra) == 0 && llStringLength(chrb)) return -1; string a = llGetSubString(chra, 0, 0); chra = llDeleteSubString(chra, 0, 0); string b = llGetSubString(chrb, 0, 0); chrb = llDeleteSubString(chrb, 0, 0); integer oa = Ord(a); integer ob = Ord(b); if(oa > ob) return 1; if(oa < ob) return -1; return wasOrdCompare(chra, chrb); } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Copyright (C) 2013 Wizardry and Steamworks - License: GNU GPLv3 // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// list wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(list BST, string root, string node) { integer i = llListFindList(BST, (list) root); string pivotRoot = llList2String(BST, i); string left = wasBinaryTreeLeft(BST, pivotRoot); string right = wasBinaryTreeRight(BST, pivotRoot); integer compare = wasOrdCompare(node, pivotRoot); if (compare > 0) { if (right == "") { if (left == "") while (llGetListLength(BST) < 2 * i + 2) BST += ""; return llListReplaceList(BST, (list) node, 2 * i + 2, 2 * i + 2); } return wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(BST, right, node); } if (compare < 0) { if (left == "") { if (right == "") while (llGetListLength(BST) < 2 * i + 1) BST += ""; return llListReplaceList(BST, (list) node, 2 * i + 1, 2 * i + 1); } return wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(BST, left, node); } llSay(DEBUG_CHANNEL, "ERROR: Invariant violation; BST must contain unique values."); return []; }
Example
Suppose that initially, we have an empty binary search tree, after which we insert the following letters in sequence: "M", "E", "R", "L", "I", "N". The resulting binary search tree should have the following structure:
M
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
E R
\ /
\ /
L N
/
I
We can test that with the script above using the following successive calls:
// start off with the empty list list in = [ "" ]; // insert M in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "M"); // insert E in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "E"); // insert R in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "R"); // insert L in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "L"); // insert I in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "I"); // insert N in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "N"); // print out the flattened tree. llOwnerSay(llDumpList2String(in, " | " ));
The result is printed out as:
[16:51] Binary Search Tree: M | E | R | | L | N | | | | I
Now, let's take "M E R L N I" and check the left and right children of every node to see whether the result is correct. As per the binary trees notation the left child of a node can be found at 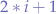 and the right child of a node can be found at
and the right child of a node can be found at 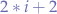 where
where i is the index of the current node.
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.



