Note
The wasBinarySearchTreeDelete function takes as arguments:
- a binary search tree (
BST) as a flattened list as per binary_trees. - the root of the binary search tree (
root) - the node (
node) to delete from the binary search tree.
and returns the resulting binary search tree.
Code

// Ord() function, written by Pedro Oval, 2010-05-28 // Inlined by Wizardry and Steamworks integer Ord(string chr) { if (chr == "") return 0; string hex = llEscapeURL(chr); if (llGetSubString(hex, 0, 0) != "%") return llBase64ToInteger("AAAA" + llStringToBase64(llGetSubString(chr, 0, 0))); integer b = (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 1, 2)); if (b < 194 || b > 244) return b; if (b < 224) return ((b & 0x1F) << 6) | (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 4, 5)) & 0x3F; if (b < 240) return (b & 0x0F) << 12 + ((integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 4, 5)) & 0x3F) << 6 + (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 7, 8)) & 0x3F; return (b & 0x07) << 18 + ((integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 4, 5)) & 0x3F) << 12 + ((integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 7, 8)) & 0x3F) << 6 + (integer)("0x" + llGetSubString(hex, 10, 11)) & 0x3F; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Copyright (C) 2013 Wizardry and Steamworks - License: GNU GPLv3 // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// integer wasOrdCompare(string chra, string chrb) { // numerical float fa = (float)chra; float fb = (float)chrb; if(fa != 0 && fb != 0) { if(fa > fb) return 1; if(fa < fb) return -1; return 0; } // lexical if(llStringLength(chra) == 0 && llStringLength(chrb) == 0) return 0; if(llStringLength(chra) && llStringLength(chrb) == 0) return 1; if(llStringLength(chra) == 0 && llStringLength(chrb)) return -1; string a = llGetSubString(chra, 0, 0); chra = llDeleteSubString(chra, 0, 0); string b = llGetSubString(chrb, 0, 0); chrb = llDeleteSubString(chrb, 0, 0); integer oa = Ord(a); integer ob = Ord(b); if(oa > ob) return 1; if(oa < ob) return -1; return wasOrdCompare(chra, chrb); } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Copyright (C) 2013 Wizardry and Steamworks - License: GNU GPLv3 // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// list wasBinarySearchTreeDelete(list BST, string root, string node) { integer i = llListFindList(BST, (list)root); string pivotRoot = llList2String(BST, i); string left = wasBinaryTreeLeft(BST, pivotRoot); string right = wasBinaryTreeRight(BST, pivotRoot); integer compare = wasOrdCompare(node, pivotRoot); if(compare > 0 && right != "") return wasBinarySearchTreeDelete(BST, right, node); if(compare < 0 && left != "") return wasBinarySearchTreeDelete(BST, left, node); if(left != "" && right != "") { integer o = llListFindList(BST, (list)node); node = wasBinarySearchTreeMinimum(BST, wasBinaryTreeRight(BST, node)); integer n = llListFindList(BST, (list)node); BST = llListReplaceList(BST, (list)node, o, o); BST = llListReplaceList(BST, (list)"", n, n); return BST; } string replace = left; if(replace == "") replace = right; integer r = llListFindList(BST, (list)replace); list FBST = llListReplaceList(llListReplaceList(BST, (list)replace, i, i), (list)"", r, r); list direct = llDeleteSubList(wasBinaryTreePreOrder(BST, replace), 0, 0); do { node = llList2String(direct, 0); direct = llDeleteSubList(direct, 0, 0); string parent = wasBinaryTreeParent(BST, node); integer p = llListFindList(FBST, (list)parent); integer d = llListFindList(FBST, (list)node); // left child if(wasBinaryTreeLeft(BST, parent) == node) { FBST = llListReplaceList(FBST, (list)"", d, d); FBST = llListReplaceList(FBST, (list)node, 2*p+1, 2*p+1); } // right child if(wasBinaryTreeRight(BST, parent) == node) { FBST = llListReplaceList(FBST, (list)"", d, d); FBST = llListReplaceList(FBST, (list)node, 2*p+2, 2*p+2); } } while(llGetListLength(direct)); return FBST; }
Example
Suppose that initially, we have an empty binary search tree, after which we insert the following letters in sequence: "M", "E", "R", "L", "I", "N". The resulting binary search tree should have the following structure:
M
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
E R
\ /
\ /
L N
/
I
We can test that with the script above using the following successive calls:
// start off with the empty list list in = [ "" ]; // insert M in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "M"); // insert E in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "E"); // insert R in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "R"); // insert L in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "L"); // insert I in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "I"); // insert N in = wasBinarySearchTreeInsert(in, "M", "N"); // print out the flattened tree. llOwnerSay(llDumpList2String(in, " | " ));
The result is printed out as:
[16:51] Binary Search Tree: M | E | R | | L | N | | | | I
Now, let's take "M E R L N I" and check the left and right children of every node to see whether the result is correct. As per the binary trees notation the left child of a node can be found at 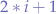 and the right child of a node can be found at
and the right child of a node can be found at 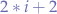 where
where i is the index of the current node.
Now we delete the "E" node:
in = wasBinarySearchTreeDelete(in, "M", "E"); llOwnerSay(llDumpList2String(in, " | " ));
and the result should be the tree:
M / \ / \ L R / / I N
Running the code, we obtain the following list:
[14:15] Binary Search Tree: M | L | R | I | | N | | | |
which is a representation for the tree that we would have expected.
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.



