This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Serve Current Directory over HTTP
The following command:
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8181
will serve the current directory where the command is executed by starting a HTTP server on port 8181.
Reverse List
The wasListReverse will reverse a list containing elements of any type.
########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2016 - License: GNU GPLv3 ## ########################################################################### def wasListReverse (l): if len(l) <= 1: return l return listReverse(l[1:]) + [ l[0] ]
Example call:
i = ["sdf", 11, 22, 39] print listReverse(i)
Output:
[39, 22, 11, 'sdf']
Derivations
Using the programming language's features, we can derive different forms of wasListReverse.
Using the Ternary Operator
The listReverseTern function makes use of the ternary operator (introduced in Python 2.5) in order to get rid of the conditional in the wasListReverse function:
########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2016 - License: GNU GPLv3 ## ########################################################################### def listReverseTern (l): return l if len(l) <= 1 else listReverseTern(l[1:]) + [ l[0] ]
Using Lambda Expressions
The listReverse lambda expression will leverage the ternary operator from the listReverseTern function and trim down the function to a single line:
########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2016 - License: GNU GPLv3 ## ########################################################################### wasListReverseLambda = lambda x : x if len(x) <= 1 else wasListReverseLambda(x[1:]) + [ x[0] ]
Example call:
wasListReverseLambda = lambda x : x if len(x) <= 1 else wasListReverseLambda(x[1:]) + [ x[0] ] print wasListReverseLambda(["sdf", 11, 22, 39])
Output:
[39, 22, 11, 'sdf']
Y-Combinator
By expressing the 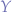 combinator using the
combinator using the 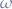 combinator as explained, the
combinator as explained, the 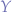 combinator can be implemented in Python.
combinator can be implemented in Python.
#!/usr/bin/python ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2016 - License: GNU GPLv3 ## ########################################################################### w = lambda x : x( x ); Y = lambda y : w( lambda f : y( lambda x : w(f)(x) ) );
An example call, to calculate the factorial of 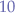 , would be:
, would be:
Factorial = Y( lambda f : lambda n : 1 if n <= 1 else n * f(n - 1) ); print Factorial(10);
Only in (Monty) Python
Memory Error When Installing Packages with Pip
In case packages cannot be installed and a MemoryError exception is thrown, then most likely it is due to pip attempting to load packages in memory. To solve the issue, run pip with the additional --no-cache-dir parameter.
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.




