This is an old revision of the document!
Von-Neumann Debiasing
Given the set of binary digits:
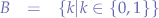
and 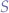 a sequence of arbitrary binary digits:
a sequence of arbitrary binary digits:
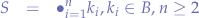
Let 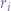 be a debiased random binary number such that:
be a debiased random binary number such that:
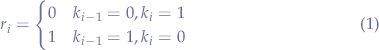
The following table shows the possible outcomes for the random binary digit 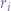 :
:
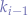 | 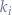 | 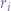 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | discard |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | discard |
Index
fuss/computer_science.1633582800.txt.gz · Last modified: (external edit)
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.



