Table of Contents
Mean vs. Median
Suppose we have a set of values 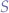 , defined as:
, defined as:
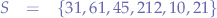
if we were to compute the arithmetic mean, we would obtain:
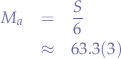
However, notice that this mean does not really look entirely "right" and that is due to the exceptional value 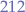 which drags the mean towards a very high value compared to the rest of the values in the set.
which drags the mean towards a very high value compared to the rest of the values in the set.
This is why, it is useful sometimes to compute the median which gives a more correct overview of the average of the set. In order to compute the median, we sort the set  in increasing order, thereby obtaining
in increasing order, thereby obtaining 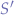 :
:
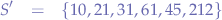
and calculate the arithmetic mean between the two values in the middle of the set:
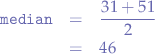
which gives us a median that is a better presentation of the middle of the original set  .
.
Standard Deviation
The standard deviation can be thought of measuring how far the data values are spread from the mean.
Let there be a random variable with mean value 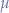
![Equations \begin{eqnarray*}
E[X] &=& \mu
\end{eqnarray*}](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/imgc55eee2c5797d231b03bac33419cda4e.png)
where the operator 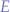 denotes the average or expected value of
denotes the average or expected value of  , then the standard deviation of
, then the standard deviation of  is the quantity:
is the quantity:
![Equations \begin{eqnarray*}
\sigma &=& \sqrt{E[X^{2}] - (E[X])^{2}}
\end{eqnarray*}](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/img0c752f8e9b682eb38e1fb4daa134e4bb.png)
Example
Given a set  of measurements with the values:
of measurements with the values:
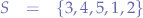
Calculate the arithmetic average 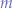 of the elements of the set:
of the elements of the set:
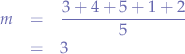
Calculate the difference squared between each element of the set  and the mean
and the mean  to obtain the set
to obtain the set  :
:
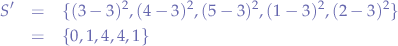
By summing up the elements of  (
(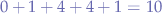 ) and then dividing by the number of elements minus one we obtain the variance
) and then dividing by the number of elements minus one we obtain the variance  :
:
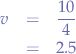
and the standard deviation  is the square root of the variance:
is the square root of the variance:
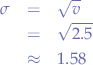
By subtracting and adding the standard deviation from the mean we found out the bounds between which most values are placed.
For the lower bound, we have:
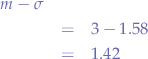
For the upper bound, we have:
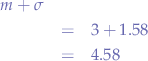
which means that most values are placed between 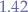 and
and 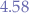 .
.
Using the Standard Deviation to Better Understand Lifespans
One of the preconceptions that float around popular culture is that lifespan is tied to genetics, environment and other factors such as wealth. Whilst the former does apply but applies more to the level of entire populations, it does not apply to individuals. For instance, one of the more "common" complaints are lifespans for males that reach up into the late 60s that are also considered unfulfilled. However, looking at the standard deviation would indicate that, for the most part, looking at the bell-curve, dying in the late 60s is just as likely as dying in the late 80s with the median line being somewhere in-between.
The chart is lifted from "optimum pensions" and traces the lifespan of women in Australia with the original article going into more details.
Even if the chart is pretty random (the only one available on Google that looked tidy) and it's application to women arbitrary, it can be observed that within two standard deviations, females in Australia are just as likely to die between the ages of 73 to 81 as they are almost just as likely to die between 97 and 105. The median instead is placed at 89, but note that all ages between the age of 73 and the age of 105 are to be found within two standard deviations, which means that  of all women in Australia die between 73 and 105, which would place an age, say, compensating for males, of 70, to be pretty much a statistically plausible age to die. Concerning the median, a person of exactly
of all women in Australia die between 73 and 105, which would place an age, say, compensating for males, of 70, to be pretty much a statistically plausible age to die. Concerning the median, a person of exactly  years is
years is  as likely to die within a range of
as likely to die within a range of 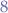 years both younger and older and only
years both younger and older and only  more likely to die beyond the median.
more likely to die beyond the median.
With that said, metrics concerning life expectancy are many times either over or underestimated and a lot of the time that takes place on subjective grounds but statistically speaking, many ages that are sometimes considered "too young", fall well-within the expected statistical distribution of a population.
Chebyshev's Theorem
The fraction of any set of numbers lying within k-standard deviation of those numbers of the mean of those numbers is at least:
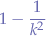
where:

and
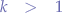
Example
Taking values for 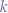 (
(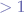 ), we can observe the following:
), we can observe the following:
- for
 , we obtain
, we obtain 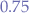 , meaning that at least
, meaning that at least 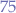 of the values must be within two standard deviations from the mean.
of the values must be within two standard deviations from the mean. - for
 , we obtain
, we obtain  , meaning that at least
, meaning that at least  of the values must be within three standard deviations from the mean.
of the values must be within three standard deviations from the mean. - for
 , we obtain
, we obtain 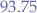 , meaning that at least
, meaning that at least  of the values must be within four standard deviations from the mean.
of the values must be within four standard deviations from the mean.
Given the previous example, we know that the mean is  and the standard deviation is
and the standard deviation is 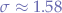 . Now we take values: for
. Now we take values: for  , we have
, we have 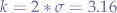 and, subtracting that value from the mean, we obtain the lower bound:
and, subtracting that value from the mean, we obtain the lower bound:  ; then we add the value to the mean, obtaining the upper bound:
; then we add the value to the mean, obtaining the upper bound:  meaning that at least
meaning that at least  of the values must be between the lower bound
of the values must be between the lower bound  and the upper bound
and the upper bound 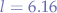 . The same can be performed for other values of
. The same can be performed for other values of  .
.
For the contact, copyright, license, warranty and privacy terms for the usage of this website please see the contact, license, privacy, copyright.




