Table of Contents
Shortnote
Project Alexandria (initially starting off as an attempt to create a library in OpenSim) is a collection of scripts that allow users to synchronize documents between OpenSim notecards and the filesystem. The project goes further by implementing a distributed search system that allows searching of imported notecards.
Presentation
In-world Location
The Project Alexandria library is part of the the VIBE grid and hosted at the University of New Orleans. It can be accessed from any OpenSim world that is capable of establishing hyperlinks by writing on the local chat:
secondlife:///repo.bio-se.info:9000/
and then opening-up the chat log and clicking that link. This will establish a hyperlink from your current grid to the library at Project Alexandria and allow you to teleport.
Alternatively, you are free to open an account on the VIBE grid from the wifi page and then setting-up the viewer by following the instructions provided on the hypergrid page on the BIO-SE wiki.
Languages and Server Configuration
The scripts are written using LSL, the OpenSim Scripting Language (OSSL) as well as in-lined mixed C#. This requires configuration changes of the OpenSim daemon but does not require changing the code of the server. The different languages are used for the following purposes:
- C# - for access to the filesystem as well as regular expression capabilities that allows searching the notecards.
- OSSL - for creating the notecards in OpenSim because LSL cannot create notecards.
The following changes have been made to the default OpenSim configuration in the OpenSim.ini file:
;; OpenSim event handlers time-out, which is not compliant ;; with the LSL specification. We thus bumped this up to 3600s (1 hour). EventLimit = 3600 ;; Because messing with the scheduler is like ;; dealing with Linux on a daily basis. Priority = "Normal" ;; This is not properly documented anywhere but we ;; assumed that it represents the script memory threshold. ;; No clue even in what it is measured, bytes, kbytes... ;; ;; We bumped this up to make sure that there will be no problems ;; reading large notecards but we do not think it is necessary. ThreadStackSize = 10385760 ;; Added C# support AllowedCompilers = "lsl,cs" ;; Enabled OSSL AllowOSFunctions = true ;; At the time of development we did not care but this could drastically ;; be lowered since only notecard OSSL functions are used. OSFunctionThreatLevel = Severe
Search System
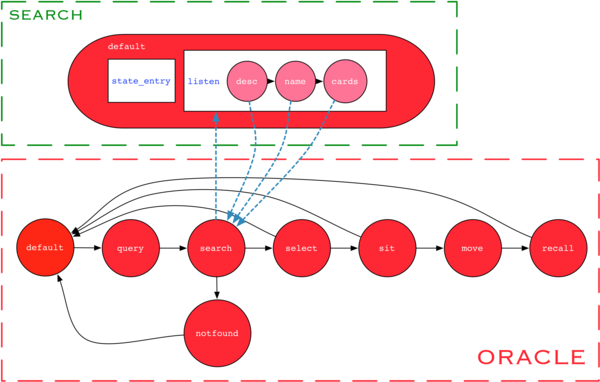
Every bookcase on Project Alexandria contains the search script that listens on a region-wide public channel for a search term provided by the oracle. Once a search term is received, every bookcase search script searches in-turn:
- the description of the bookcase (the author name).
- the name of the bookcase.
- the names of the notecards.
Once a result is found, the position and the name of the bookcase is broadcasted on a different channel, on which the oracle script listens to.
Once a result is received by the oracle, the result is stored and the oracle uses an alarm to reschedule the transition from the search and to the select state. This is performed in order to give all bookcases a chance to return results. Similarly, all transitions from the select and sit states to the default state allow the corresponding operations to time out.
We can observe the implicit states desc, name and cards in the listen event handler of the search script. These are the implicit states where the search script searches the description and name of the object as well as the names of the notecards. The listen event handler can also be extended to search, for example, within the actual text of the notecard.
Security Notes
Using C# in OpenSim grants any user direct access to the filesystem - this is a major concern since any file on the server filesystem could then be extracted through OpenSim. To prevent this, specify the following parameters in the OpenSim.ini configuration file, in the [Startup] section:
[Startup] GrantLSL = 5998029f-ddde-4497-b3e1-b7a5d702742f,b02e3094-a3c6-4921-8dcf-5c33aea6c261 GrantCS = 5998029f-ddde-4497-b3e1-b7a5d702742f,b02e3094-a3c6-4921-8dcf-5c33aea6c261 GrantVB = 5998029f-ddde-4497-b3e1-b7a5d702742f,b02e3094-a3c6-4921-8dcf-5c33aea6c261 GrantJS = 5998029f-ddde-4497-b3e1-b7a5d702742f,b02e3094-a3c6-4921-8dcf-5c33aea6c261 GrantYP = 5998029f-ddde-4497-b3e1-b7a5d702742f,b02e3094-a3c6-4921-8dcf-5c33aea6c261
where the UUIDs 5998029f-ddde-4497-b3e1-b7a5d702742f and b02e3094-a3c6-4921-8dcf-5c33aea6c261 represent agent IDs that are allowed to use the respective languages.
It is imperative to well-define the agents that will be allowed to use the compilers you enable with the AllowedCompilers setting; otherwise, any agent will have full access to the filesystem.
Caveats
- The viewer may have issues opening large notecards depending on the quality of the connection between the viewer and the server. The real issue is that notecards are downloaded by the viewer just like any other asset. Thus, very large notecards may take a long time to download depending on their size and the quality of the connection between the client and the server.
File Transfer
- File-transfer in the demonstration shown in the video is done manually over
ssh. This can be extended by using software such as WinSCP that gives the user a nice drag and drop interface to upload text files.
- DropBox is also an alternative, provided that the mount path (in our case
/home/opensim/books) is substituted for the DropBox folder under Linux. This is perhaps the easiest and cleanest method without requiring uploaders to configure asftpclient.
DropBox
This section covers installing DropBox for Linux and setting up a sync between /home/opensim/books and the DropBox folder. First we get and install DropBox along with all the required dependencies.
wget -O dropbox_1.4.0_amd64.deb -c https://www.dropbox.com/download?dl=packages/debian/dropbox_1.4.0_amd64.deb aptitude install python-gtk2 python-gpgme dpkg -i dropbox_1.4.0_arm64.deb
Next, we configure DropBox with:
dropbox start -i
which will ask for the proprietary daemon to be downloaded.
Now, we download the CLI DropBox client:
wget -O dropbox.py -c https://www.dropbox.com/download?dl=packages/dropbox.py mv dropbox.py /usr/local/bin/ chmod +x /usr/local/bin/dropbox.py
And we link the computer to a DropBox account (we can create a brand new one):
To link this computer to a dropbox account, visit the following url: https://www.dropbox.com/cli_link?host_id=529ca8050a00180790cf88b63468826a
by visiting the indicated URL.
Now we start the dropbox daemon:
~/.dropbox-dist/dropboxd
The result is that a new folder is created in the user's home directory called Dropbox. In our case, we copied the files from /home/opensim/books to /home/opensim/Dropbox/books and then created a soft link from the Dropbox folder to books:
ln -sf Dropbox/books books
The reason why a subfolder Dropbox/books was created is because DropBox does not allow sharing the entire account.
DropBox Startup Script
Assuming that the Linux distribution is Debian, DropBox can be started with a shell script found on the DropBox wiki. The following script can be copied to /etc/ini.d/dropbox:
- dropbox
#!/bin/sh ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: dropbox # Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $syslog $named # Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $syslog $named # Default-Start: 2 3 4 5 # Default-Stop: 0 1 6 # X-Interactive: false # Short-Description: dropbox service ### END INIT INFO #dropbox service DROPBOX_USERS="opensim" DAEMON=.dropbox-dist/dropbox start() { echo "Starting dropbox..." for dbuser in $DROPBOX_USERS; do HOMEDIR=`getent passwd $dbuser | cut -d: -f6` if [ -x $HOMEDIR/$DAEMON ]; then HOME="$HOMEDIR" start-stop-daemon -b -o -c $dbuser -S -u $dbuser -x $HOMEDIR/$DAEMON fi done } stop() { echo "Stopping dropbox..." for dbuser in $DROPBOX_USERS; do HOMEDIR=`getent passwd $dbuser | cut -d: -f6` if [ -x $HOMEDIR/$DAEMON ]; then start-stop-daemon -o -c $dbuser -K -u $dbuser -x $HOMEDIR/$DAEMON fi done } status() { for dbuser in $DROPBOX_USERS; do dbpid=`pgrep -u $dbuser dropbox` if [ -z $dbpid ] ; then echo "dropboxd for USER $dbuser: not running." else echo "dropboxd for USER $dbuser: running (pid $dbpid)" fi done } case "$1" in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; restart|reload|force-reload) stop start ;; status) status ;; *) echo "Usage: /etc/init.d/dropbox {start|stop|reload|force-reload|restart|status}" exit 1 esac exit 0
and then activated with:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/dropbox update-rc.d dropbox defaults
which will make sure that DropBox starts on boot.
Index
The components are explained further on their individual pages. Additionally, we use the giver project to hand out the notecards.