Table of Contents
Polynomial Expansions
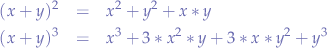
Binomial Formula

Implementations
Linearly Map a Value in a Range into another Range
Given a value  such that
such that ![Math $s \in [a_{1},a_{2}]$](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/imgb9d572ef407bb459c37e1acf65476172.png) we can map
we can map  onto a different range such that
onto a different range such that ![Math $s \in [b_{1}, b_{2}]$](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/imge37c3f2bde53a19f35ffb53a5cfeb7e4.png) by using the formula:
by using the formula:
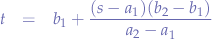
Implementations
Invert a Range
Given a range 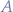 represented as an ordered set
represented as an ordered set  , the inverted-range ordered set
, the inverted-range ordered set 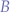 is obtained using the formula
is obtained using the formula  such that
such that  where
where  is a function that returns the largest element in a set.
is a function that returns the largest element in a set.
Or, in other words, the set  is the sequential union of all elements
is the sequential union of all elements  obtained via the formula
obtained via the formula  as follows:
as follows:

Clamp a Random Number to a Range
Given an arbitrary random number  , in order to obtain a random number
, in order to obtain a random number 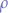 such that
such that ![Math $\rho \in [min, max], \rho:X \mapsto [min, max]$](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/img9814141911ae08bd8a735f1b19be4054.png) and notice that
and notice that  , the following formula can be used:
, the following formula can be used:
![Equations \begin{eqnarray*}
\rho_{[min,max]} = min + r \% ( max - min + 1 )
\end{eqnarray*}](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/img1c17356e5985d9ff88a57286c93d52b4.png)
where:
 represents the remainder division of the two left operands (in this case
represents the remainder division of the two left operands (in this case  ) and right operands (
) and right operands ( )
)