Table of Contents
Docker
Reasons for Using Docker
- The new paradigm that Docker introduces that is most useful is the prioritization of data over software.
- In other words, due to the amount of available software, a very large trend has been to adhere to certain software packages, like being part of a fandom of brands, when, in fact, any software that can solve a problem and generate, and / or process, some desired data is a great software to use. The adulation of software over data is over with Docker.
- Linux was never designed with tidiness in mind (except for definitions like the FSH, that came later) such that it is fully expected to unpack all the crap in /bin or on top of / and then just deal with the fallout when some file goes astray and starts creating problems. For that reason, Docker is a great solution because it keeps all the requirements for whatever software is run within a container without polluting the operating system. In some ways, it is the only "sandboxing" feature, with less requirements than hypervisor virtualization and more management tools than a common root-jail, that Linux ever had.
- There is a lot of software that has been created across the years by people with varying backgrounds in computer science, a lot of the software being, in fact, created by scientists working in natural sciences, that tend to churn over obscure libraries with esoteric requirements, either obsolete, hard to find, and mostly hard to recompile, such that a lot of the time, you really just want to get the software up and running without delving into the ins and outs of how a package is compiled. Unfortunately, the sound of the other shoe is that by containerizing, the software runs in a black box and a very tangential consequence, yet pertinent, is that the user is unable to assess how bad the software really is in terms of quality. Sometimes, software that is too difficult to compile, should just not be used.
- There is a corollary to the former where ironically some software is so badly designed that Docker even seems to complicate the matters further (sometimes, people even suspect that is done deliberately in order to maintain control over the project).
Reasons for Not Using Docker
- Whilst Docker does its best to mask itself as open-source and being deeply involved with the "community", the reality is that docker is a private company whose decisions might not necessarily align with the decisions of the "community", nor with open-source dialectics (remember when Google made the 20-year old free translation service non-free, overnight and started charging for it such that there is probably a large slice of the Internet that still contains third-party translators made to work with Google translate that can now just be scrapped because they will never work again?).
- The first warning (concerning docker) a user gets is when they start working with docker and find out for the very first time that their pull requests are, in fact, limited and in order to pull containers more often, the users need to sign up and additionally, for some setups, become paying customers,
- Unless the user takes it upon themselves to recompile everything and build containers themselves (there are a few...), pre-made containers are available from a vast array of third-party individuals that may or may not either update the container with the new software, or also not slide backdoors into containers that are made public.
- The typical mitigation is to only use official containers, yet that is not always possible and the task to containerize every single application seems fairly daunting, even in terms of workload.
- Unless users partition their containers, there is a lot of data, and now with the docker paradigm, service-deduplication, where two containers might contain the same software (ie: the same database engine).
- The typical mitigation for this is to split containers up, manually, yet this leads back to the same problem of having the extra workload of (even) breaking up official containers.
- On the low-level, docker containers are treated as disposable, and interaction with the software inside is rather brutal. For example, when a container is shut down, the entire environment is just torn away and disposed, thereby potentially leaving static data in an unknown state (one example thereof is terminating a container whilst a program inside the container holds one file open, leading to possibly trashing the file when the handle is removed abruptly), other examples include the corruption of databases such as SQLite that make a point out of being gracefully opened and gracefully closed for the sake of a consistent (deterministic) workflow.
- There are some semantic lacks that are justified with a lot of dark magic; for instance, there is no way to "just restart" a container within a swarm, the only way to "restart" is to just dispose the entire environment and then re-create it from scratch, the justification thereof being a bleak mention on how containers in the swarm "are just sent out there" so they cannot be restarted (compared to containers without a swarm, that can indeed be restarted via "start" and "stop").
- Typically, every single "fix" that is suggested, involves tearing down the setup and then, admittedly using scripts, recreating the environment from scratch thereby potentially occluding setup mistakes and architectural bad choices, even involving the usage of docker.
- Even though the docker swarm has (had?) potential, one architectural problem is that the swarm is designed to have a handful of "managing nodes", and a plethora of "worker nodes" with the "managing nodes" being the only ones capable of pushing containers to a swarm as well as performing other administrative tasks. This is a design flaw, and a missed opportunity, because all the (few) "managing nodes" become single points of failure and then the entire swarm will need a central managing system (even if multiple managing nodes, consisting of the managing nodes themselves) (making all nodes manager nodes does not work as a workaround to obtain a P2P-like topology!).
- Another problem with the docker swam is that there is no way to perform tasks that should be possible (in fact, some of these tasks are "possible", but via various commands that ... hack the result):
- migrating a container onto a given node is not possible,
- balancing the swarm across the cluster is performed by some crutch-command that is really just meant to refresh the container, not to make the swarm balance itself,
- (even though this requires extra code) there is no way to let the swarm automatically balance and re-balance itself depending on what machine containers end up on, the only attainable balancing algorithm being just an equal-share spread of containers across machines, but without accounting for the necessary computational requirements of the containers themselves (ie: distribute a workload / CPU bound heavy container to a more powerful machine),
- The networking side of docker seems to be neatly brushed under the carpet where opening up containers in certain ways or deploying to a swarm ends up creating various network bridges, overlay networks and other paraphernalia resulting sometimes even in cutting off the server's connection to the local network, as well as generating "redundant networks" with containers ending up with multiple IP addresses.
- Networks seem to always be created in the class A private address space (
10...) such that if any such network already exists, just installing docker and starting a container will interfere with the local networks. - It is very difficult to customize low-level properties of the networks created by Docker, simply because the design of Docker extends to multiple domains (applications, networking, etc) without fully covering all the usage cases. For example, it is very difficult to configure Docker to set a custom MTU for the various interfaces it creates and typically one would resort to udev to create rules to configure the interfaces.
- On a philosophical level, docker tends to phase out the importance of various software packages, and makes all the talk about "just installing a bunch of applications" - so the official Apache docker does not contain a module you need? Doesn't matter, scrap the container and find some third-party re-packaged Apache container and use that instead. The result thereof is hiding the need to be well-acquainted or experienced with well-established Linux software packages (Apache, Bind, ISC DHCP) and then adding the philosophy of "just scrapping" the current workflow makes docker the ultimate tool of dumbing down IT in general.
- There is a problem with precedence (or clash of interests) when accounting for software that has an update feature because Docker would rather have the user upgrade the container itself rather than the application within updating itself. Depending on who packaged the application, a container update might not appear as soon as it would be desirable compared to the built-in application update feature.
- The security gained via containerization is also security lost due to many containers being built using outdated or obsolete distribution versions that do not receive any more security updates and are hence vulnerable forever.
Reasons for Not Using Docker Swarm
- Due to its lack of orchestration, or rather due to the only available orchestration for Docker Swarm being "spread", which spreads out services equally amongst all available nodes but does not perform any ulterior accounting, Docker Swarm currently suffers from a hard-NP problem that would lead to uneven resource usage across a cluster. In layman terms, it is impossible to account for the runtime resource usage of applications, such that the resource usage should be monitored and services redistributed accordingly, but Docker Swarm does not track resource utilization after the initial placement of a service such that it is entirely possible to obtain a runtime topology where a certain node is completely overloaded in terms of resources whilst the other nodes do not use any resources at all. Docker does perform an initial resource usage check across all nodes, even corresponding to pre-configured values, but does not perform any ulterior tracking, such that, at best, in case the user hard-limits every single service, there will be no catastrophic failure of a single node, however it is still possible and more than likely to obtain an uneven distribution of resource usage across a cluster.
Docker Templates
Automatically Update Container Images
The Watchtower container can be ran along with the other containers, will automatically monitor the various docker containers and will then automatically stop the containers, update the image and restart the containers.
Similarly, for swarms, shepherd is able to be deployed in order to update containers for which a Wizardry and Steamworks guide exists.
Rebalance Swarm
The following command:
docker service ls -q | xargs -n1 docker service update --detach=false --force
will list all the services within a swarm and then force the services to be re-balanced and distributed between the nodes of the swarm.
After executing the command, all nodes can be checked with:
docker ps
to see which service got redistributed to which node.
One idea is to run the rebalancing command using crontab in order to periodically rebalance the swarm.
Maintaining an Even-Distribution of Services Across the Swarm
Unfortunately, services do not spread evenly through the swarm such that re-balancing is necessary. In fact, the strategy of distributing services across the swarm is surprisingly bad, with the manager node taking upon itself most of the services and with very few left over to the last node of the swarm. It seems Docker spreads services on a bucket-fill-like strategy where services are only spread out if the current node is deemed somehow full.
Irrespective of the lack of a strategy, here is one constructed command:
docker service ls | \ awk '{ print $1 }' | \ tail -n +2 | \ xargs docker service ps --format "{{.Node}}" --filter "desired-state=running" | \ awk ' { node[$0]++ } END { for (i in node) print node[i] } ' | \ awk '{ x += $0; y += $0 ^ 2 } END { print int(sqrt( y/NR - (x/NR) ^ 2)) }' | \ xargs -I{} test {} -gt 2 && docker service ls -q | xargs -n1 docker service update --detach=false --force
that performs the following operations in order:
- retrieves the services in the swarm,
- gets the number of services running per node,
- computes the standard deviation of the services running per node,
- if the standard deviation is greater than
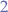 then the rebalancing command is ran in order to distribute services across the swarm.
then the rebalancing command is ran in order to distribute services across the swarm.
In other words, the distribution strategy of the cluster is to place an equal share of services per available nodes.
Intuitively, the command can be placed in a cron script and, compared to just calling the swarm re-distribution command, the script should have no effect when the services are distributed evenly across the nodes due to the standard deviation falling well under  (with
(with 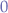 being the theoretical point that the standard deviation should be when the services are evenly spread out).
being the theoretical point that the standard deviation should be when the services are evenly spread out).
Restarting Services instead of Updating Services
Sometimes it seems that services that are just updated do restart but for some reason end up in an unexpected state such that restarting the service entirely seems like a better option. For that purpose, the following script should achieve that job.
#!/usr/bin/env bash ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2025 - License: MIT ## ## Please see: https://opensource.org/license/mit/ for legal details, ## ## rights of fair usage, the disclaimer and warranty conditions. ## ########################################################################### # The following program is designed to check whether services are equally # # distributed across a Docker swarm and in case they are not, the program # # will restart the services in order to allow Docker to distribute the # # services to less busy nodes. Note that this program does not use the # # usual scale-up / scale-down trick to distribute services due to some # # services not properly initializing after a scale-up / scale-down event. # # # # Requirements: # # * yq # # # # The script requires that a specific filesystem structure is in place # # such that compose files might have to be reorganized in order for the # # script to work properly. # # # # Root # # + # # | # # +----+ stack_dir1 # # | # # +----+ stack_dir2 # # | | # # | +--------+ compose_file1 # # | | # # | +--------+ compose_file2 # # . . . # # . . . # # . . . # # | # # +----+ ignore_dir # # # # the root corresponds to the DOCKER_COMPOSE_ROOT variable and under that # # directory, several directories can be added whose names should be a # # stack name stack_dir1, stack_dir2, etc. The stack directories will then # # contain compose files that define services that will run under the # # stack name given by the directory that they are in. # ########################################################################### ########################################################################### ## CONFIGURATION ## ########################################################################### # the root to the special Docker filesystem DOCKER_COMPOSE_ROOT=/mnt/docker/compose # the whole or part of a stack directory name that will be ignored IGNORE_NAME=parked ########################################################################### ## INTERNALS ## ########################################################################### # Acquire a lock. LOCK_FILE='/var/lock/docker-swarm-rebalance' if mkdir "$LOCK_FILE" &>/dev/null; then trap '{ rm -rf $LOCK_FILE; }' QUIT TERM EXIT INT HUP else exit 0 fi # check if services are unevenly balanced and terminate successfully if they are balanced docker service ls | \ awk '{ print $1 }' | \ tail -n +2 | \ xargs docker service ps --format "{{.Node}}" --filter "desired-state=running" | \ awk ' { node[$0]++ } END { for (i in node) print node[i] } ' | \ awk '{ x += $0; y += $0 ^ 2 } END { print int(sqrt( y/NR - (x/NR) ^ 2)) }' | \ xargs -I{} test {} -gt 2 || exit 0 # run through all docker services and restart them all find "$DOCKER_COMPOSE_ROOT" -maxdepth 1 -mindepth 1 -type d ! -name "$IGNORE_NAME" | while read STACK_DIRECTORY; do STACK_NAME=`basename $STACK_DIRECTORY` find "$STACK_DIRECTORY" -type f ! -name ~* | while read COMPOSE_FILE; do SERVICE_NAME=`yq -r '.services | keys[]' < "$COMPOSE_FILE"` docker service rm "$STACK_NAME""_""$SERVICE_NAME" sleep 1 docker stack deploy --detach=True -c "$COMPOSE_FILE" "$STACK_NAME" done done
Note that the header contains instructions on organizing docker compose files into directories named after the stack that they are supposed to run under.
Run a Shell in a Container within a Swarm
Typically, to open a console, the user would write:
docker run -it CONTAINER bash
where:
CONTAINERis the name or hash of the container to start "bash" within
However, given that containers are distributed in a swarm, one should first locate on which node the container is running by issuing:
docker service ps CONTAINER
where:
CONTAINERis a container running in the swarm
The output will display in one of the columns the current node that the container is executing on. Knowing the node, the shell of the node has to be accessed and then the command:
docker ps
can be used to retrieve the container ID (first column).
Finally, the console can be started within the distributed container by issuing:
docker exec -it CONTAINER_ID sh
where:
CONTAINER_IDis the id of the container running in the swarm on the local node
Pushing to Private Registry
The syntax is as follows:
docker login <REGISTRY_HOST>:<REGISTRY_PORT> docker tag <IMAGE_ID> <REGISTRY_HOST>:<REGISTRY_PORT>/<APPNAME>:<APPVERSION> docker push <REGISTRY_HOST>:<REGISTRY_PORT>/<APPNAME>:<APPVERSION>
Restart Docker if Worker cannot Find Swarm Manager
If a worker cannot find the swarm manager when it starts up, at the current time of writing, Docker is made to terminate. This is problematic because the manager might go online after a while such that the workers should just wait to connect.
On some Linux distributions, such as Debian, Docker is started via a service file located at /lib/systemd/system/docker.service and it can be copied to /etc/systemd/system with some modifications in order to make SystemD restart Docker if it terminates.
On Debian, the service file is missing the RestartSec configuration line, such that it should be added to /etc/systemd/system/docker.service after being copied. Here is the full service file with the added line:
[Unit] Description=Docker Application Container Engine Documentation=https://docs.docker.com After=network-online.target docker.socket firewalld.service containerd.service Wants=network-online.target containerd.service Requires=docker.socket [Service] Type=notify # the default is not to use systemd for cgroups because the delegate issues still # exists and systemd currently does not support the cgroup feature set required # for containers run by docker EnvironmentFile=-/etc/default/docker ExecStart=/usr/sbin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock $DOCKER_OPTS ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID LimitNOFILE=1048576 # Having non-zero Limit*s causes performance problems due to accounting overhead # in the kernel. We recommend using cgroups to do container-local accounting. LimitNPROC=infinity LimitCORE=infinity # Uncomment TasksMax if your systemd version supports it. # Only systemd 226 and above support this version. TasksMax=infinity TimeoutStartSec=0 # set delegate yes so that systemd does not reset the cgroups of docker containers Delegate=yes # kill only the docker process, not all processes in the cgroup KillMode=process # restart the docker process if it exits prematurely Restart=on-failure StartLimitBurst=3 StartLimitInterval=60s RestartSec=10s [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
With this change, SystemD will try to bring Docker up every 10s after it has failed. Unfortunately, this fix has to be applied for all nodes in a Docker swarm.
Building using The Distributed Compiler
Some packages have to be compiled manually such that it is beneficial to use a distributed compiler in order to distribute the compilation workload across multiple computers. However, the system should be flexible enough to include the edge case when a distributed compiler is not available.
To that end, here is a Dockerfile that is meant to define some variables such that "distcc" will be used to distribute the compilation across a range of computers:
FROM debian:latest AS builder
# define compilation variables
ARG DISTCC_HOSTS=""
ARG CC=gcc
ARG CXX=g++
# install required packages
RUN apt-get --assume-yes update && apt-get --assume-yes upgrade && \
apt-get --assume-yes install \
build-essential \
gcc \
g++ \
automake \
distcc
# ... compile ...
RUN DISTCC_HOSTS="${DISTCC_HOSTS}" CC=${CC} CXX=${CXX} make
and the invocation will be as follows:
docker build \
-t TAG \
--build-arg DISTCC_HOSTS="a:35001 b:35002" \
--build-arg CC=distcc \
--build-arg CXX=distcc \
.
where:
TAGis a tag to use for the build (can be used to upload to a registry),DISTCC_HOSTS,CCandCXXare the environment variables setting the compiler todistccand the hosts to be used to compile (in this case, computersaandblistening on port35001and35002)
If you would like a ready-made container for distcc, you can use the Wizardry and Steamworks build.
Opening up a Port Across Multiple Replicas
Even though multiple replicas of a container can exist even on the same system or spread out through a swarm, due to the nature of TCP/IP a single port might be allocated at the same time for any single process, such that when starting a series of clones of a program, there must exist a way to specify a port range or a series of ports for each instance of the program being launched.
The syntax is as follows:
START_PORT-END_PORT:CONTAINER_PORT
where:
START_PORTandEND_PORTdelimit a range from a starting port to an ending port that the clones of the programs will use to select their listening outbound port and,CONTAINER_PORTrepresents the port for the program running within the container that will be exposed.
Interestingly, this feature does not work as expected and whilst the ports will be used for all nodes within the swarm for all replicas of the service, all ports will be replicated by all nodes such that accessing one port within the port range successively will lead to a service on a different node within the docker swarm. If stickyness is desired, the current solution at the time of writing is to either use jwilder/nginx-proxy or to just declare multiple services of the same image with the constraints set appropriately to each node in the swarm.
Restarting Containers on a Schedule
Depending on the application, in some rare cases some containers must be restarted. For example, invidious documents stat that invidious should be restarted at least once per day or invidious will stop working. There are multiple ways to accomplish that, either by using the system scheduling system, such as cron on Linux, but the most compact seems to use docker-cli and trigger a restart of the service. For example, the following additional service can be added to the invidious service in order to restart invidious at 8pm:
invidious-restarter:
image: docker:cli
restart: unless-stopped
volumes: ["/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"]
entrypoint: ["/bin/sh","-c"]
command:
- |
while true; do
if [ "$$(date +'%H:%M')" = '20:00' ]; then
docker restart invidious
fi
sleep 60
done
When running under a swarm, it gets a little more complicated due to the controlling service only being present on master nodes such that the supplementary service has to only be deployed on master nodes in order to restart the service. Here is the modified snippet:
invidious-restarter:
image: docker:cli
restart: unless-stopped
volumes: ["/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"]
entrypoint: ["/bin/sh","-c"]
deploy:
replicas: 1
placement:
constraints:
- node.role == manager
command:
- |
while true; do
if [ "$$(date +'%H:%M')" = '20:00' ]; then
docker service ls --filter name=general_invidious --format "{{.ID}}" | \
head -n 1 | \
xargs -I{} docker service update --force --with-registry-auth "{}"
fi
sleep 60
done
that will make sure that the general_invidious service will be restarted every day at 8pm.
Docker Swarm - Server Contingencies
Here are some useful changes to mitigate various issues with running a Docker swarm:
- RAM and OOM
- Docker does not take the available amount of RAM per machine into account such that any process that is distributed to a machine that will end up consuming more RAM than the machine has available, will simply end up using up all the RAM on that machine till the machine hangs. An additional OOM killer such as the SystemD OOM killer could be used to attempt to prevent a process started by Docker to grind the machine to a halt.
- CPU and hangs
- The hangcheck-timer module could be used in the absence of a hardware watchdog to reboot the machine in case the machine has stalled for a long time.
- Linux control-groups can be used in order to limit the total amount of CPU and RAM allocated to Docker as a whole because Docker does not implement any upper limit itself. This would have to be tailored to all nodes in a Docker swarm.
- Storage
- nodes will be similar to storageless thin-clients mounted over NFS, such that log files on each node should be irrelevant. Trimming the logs down in size, in particular under SystemD systems that tend to set a very large log size is good idea.
Dumping Running Container Process Identifier to Files
The following script was written in order to query the currently running containers on a machine running Docker and then create a directory and write within that directory PID files containing the PIDs of the services being ran within the Docker container.
The script was used for monitoring services on multiple machines in a Docker swarm where it was found necessary to retrieve the PID of the services within a Docker container without breaking container isolation.
#!/usr/bin/env bash ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2024 - License: MIT ## ########################################################################### # path to the swarm state directory where PID files will be stored STATE_DIRECTORY=/run/swarm if [ ! -d $STATE_DIRECTORY ]; then mkdir -p $STATE_DIRECTORY fi DOCKER_SWARM_SERVICES=$(docker container ls --format "{{.ID}}" | \ xargs docker inspect -f '{{.State.Pid}} {{(index .Config.Labels "com.docker.stack.namespace")}} {{(index .Config.Labels "com.docker.swarm.service.name")}}') while IFS= read -r LINE; do read -r PID NAMESPACE FULLNAME <<< "$LINE" IFS='_' read -r NAMESPACE NAME <<< "$FULLNAME" PIDFILE="$STATE_DIRECTORY/$NAME"".pid" if [ ! -f "$PIDFILE" ]; then echo $PID >"$PIDFILE" continue fi test $(cat "$PIDFILE") -eq $PID || \ echo $PID >"$PIDFILE" done <<< "$DOCKER_SWARM_SERVICES"
Searching Logs on the Command Line
It seems that the Docker logs command will print out the logs on stderr such that piping the output to grep or other tools will not work properly. In order to making piping work, stderr has to be redirected to stdout and then piped to whatever tool needs to be used:
docker service logs --follow general_mosquitto 2>&1 | grep PING
Repositories not Signed in Docker Container
Sometimes the reason behind the errors claiming that repositories are not signed during a Docker build are due to the lack of space on the hard-drive. The errors are along the line of:
#7 0.692 Get:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm InRelease [151 kB] #7 0.771 Get:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm-updates InRelease [55.4 kB] #7 0.814 Get:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security InRelease [48.0 kB] #7 0.869 Err:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm InRelease #7 0.869 At least one invalid signature was encountered. #7 0.954 Err:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm-updates InRelease #7 0.954 At least one invalid signature was encountered. #7 1.066 Err:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security InRelease #7 1.066 At least one invalid signature was encountered. #7 1.101 Reading package lists...
Healthcheck within Docker Compose file vs. Healthcheck within Dockerfile
Both Docker compose files and Dockerfiles allow the creation of health checks and the difference is that health checks placed within compose files will be executed by the host and thus cannot access the inside of the Docker container whilst health checks within Dockerfiles take place inside the container.
If possible, it is always preferable to create health checks within a Dockerfile when building a container image mainly because this represents a separation of concerns and also respects the containerization principle of software running with Docker.
Getting Docker UTF-8 Support on Debian
Some software requires the console to be set to UTF-8, in particular software that deals with the Linux command line such as Jenkins. By default the debian or debian-slim images are configured to have a POSIX locale by default, such that the locale has to be changed to UTF-8 during the build process of the image.
The following snippet should be inserted into a Dockerfile that inherits from debian or debian-slim images in order to set the locale to UTF-8:
# UTF-8 support
RUN apt-get install -y coreutils locales && \
sed -i -e 's/# en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8/' /etc/locale.gen && \
locale-gen && \
dpkg-reconfigure --frontend=noninteractive locales && \
update-locale LANG=en_US.UTF-8
# set environment variables
ENV LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
ENV LANG=en_US.UTF-8
ENV LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8
Docker Resource Consumption Accounting using Linux Control Groups
Docker implements special support for c-groups in order to allow controlling the resource usage of Docker itself. In order to enable c-groups, edit or create /etc/docker/daemon.json in order to add the following contents:
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"cgroup-parent": "docker_limits.slice"
}
The configuration will:
- enable the native SystemD c-groups driver,
- use
docker_limits.sliceto mitigate the resource consumption.
In turn, the file docker_limits.slice is placed at /etc/systemd/system/docker_limits.slice and contains the following:
[Unit] Description=Slice that limits Docker resources Before=slices.target [Slice] CPUAccounting=true CPUQuota=90% MemoryAccounting=true MemoryHigh=2G MemoryMax=2.5G
that enables both CPU and RAM accounting, sets the maximum CPU usage to  and the maximum memory consumption to
and the maximum memory consumption to  .
.
Lastly, in order to check the RAM usage of Docker, the systemd-cgtop tool can be used that displays the resource consumption for c-groups.
Docker Services "Just Not Starting" in a Docker Swarm
Docker on its own performs no accounting in terms of services running within a Docker swarm and the only distribution strategy of services is an equal "spread" of services. Depending on what node is up and at what time, the distribution of services is not even equal to all nodes such that fairer end-user service distribution solutions make sense to keep a balance of services across a set of nodes.
However, even with equally distributed services, Docker does not and can not know what amount of CPU or RAM a service might require at runtime such that a runtime solution to shift services around in a swarm would make more sense. One way to check the CPU consumption is to check all the services and see what total CPU usage they collectively generate and then repeat the same procedure for RAM and/or other resources that the services might consume.
Without accounting for resource consumption it often happens for the Docker managers of a swarm to place services on the same node within a swarm such that the node ends up overloaded and without the ability to answer requests. This section explores possibilities to mitigate such Denial of Service issues that stem from the inability to predict the amount of resource usage head of time in order to ensure that services placed on a node do not end up slowing the node down due to their high resource consumption patterns.
Pinning
Similar to multitasking solution, one obvious solution is to pin the heavy services to different nodes in order to ensure that they do not all run together. This would work by changing the service constrains to pin the service to different nodes.
Here is a snippet from a Docker compose service:
deploy: labels: - shepherd.enable=true - shepherd.auth.config=docker replicas: 1 placement: max_replicas_per_node: 1 constraints: - node.hostname == docker2
where the node.hostname == docker2 constraint makes sure that the service will run on the node with the hostname docker2.
Although this is a fine solution, it will not work in terms of load-balancing and adaptability because when the node docker2 becomes unavailable, the Docker managers would simply not know where to place the service. Furthermore, manually pinning services to nodes adds a level of locality that is unbecoming of a cluster - in other words, if all services are pinned, why even bother running a cluster and not just run the software on the nodes directly?
By Specification
Fortunately, Docker does perform the minimal level of accounting necessary in order to be aware of how many resources the node has such that working by specification, which is the best option, is very much possible. Here is an example excerpt out of a Docker compose service:
deploy: labels: - shepherd.enable=true - shepherd.auth.config=docker replicas: 1 placement: max_replicas_per_node: 1 # constraints: # - node.hostname == docker2 resources: reservations: cpus: '1' memory: 1G
Now, instead of pinning the service to the node with the hostname docker2, the service is defined (or specified) to require a full core (cpus: '1') and also require  of RAM. Now, when the service is deployed to the swarm, each node that is a potential candidate for deployment will cross-check the requirements with the resources available, and, if the required amount of CPU and RAM are not met, the node will reject the service. This process shall carry on until a node either accepts the service or the service enters a fail state that can be observed with
of RAM. Now, when the service is deployed to the swarm, each node that is a potential candidate for deployment will cross-check the requirements with the resources available, and, if the required amount of CPU and RAM are not met, the node will reject the service. This process shall carry on until a node either accepts the service or the service enters a fail state that can be observed with docker ps that will hint that no solution is available that would match the deployment requirements.
It is not even required to provide a specification for all services, adding the requirements for services that seem to generate heavy load should be sufficient.
Automatic Configuration Reload for Docker Software
Typically *nix daemons are not meant to restart or reload themselves especially as a consequence of a changed configuration, which means that software running within a Docker container will require the Docker container to be restarted in order for the daemon to reload its configuration. It is however possible to implement a generic solution that should work across the board for any sort of software running within a container based on filesystem primitives such as INOTIFY.
The script is fairly simple and consists in just one command watching a directory and then raising an alarm when files are changed within that directory:
#!/usr/bin/env bash ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2024 - License: MIT ## ########################################################################### # This script can be used to make a daemon reload its configuration # # whenever a change occurs within a defined directory, presumably the # # same directory where the configuration is stored in the first place. # # # # The script requires the "inotify-tools" package to be installed or # # whatever other package provides the "inotifywait" command line tool. # # Next, the script must be modified to make the necessary changes in the # # "CONFIGURATION" section where the path to the directory to be watched # # is specified and to also define a command that should be used to reload # # the daemon. Note that whatever the command contains, must also be # # installed for the script to work. # # # # The script has to be ran permanently for the entire duration that the # # processes that it is monitoring is running. This can be accomplished by # # starting the script using "supervisord" or any other tool that can run # # daemons, including bash scripts. # ########################################################################### ########################################################################### # CONFIGURATION # ########################################################################### MONITOR_DIRECTORY=/data RELOAD_COMMAND="kill -s HUP `pidof freeradius`" ########################################################################### # INTERNALS # ########################################################################### # alarm(2) function alarm { sleep $1 eval $RELOAD_COMMAND } ALARM_PID=0 trap '{ test $ALARM_PID = 0 || kill -9 $ALARM_PID; }' KILL QUIT TERM EXIT INT HUP inotifywait -q -m "$MONITOR_DIRECTORY" -r \ -e "modify" -e "create" -e "delete" | \ while IFS=$'\n' read -r LINE; do if [ -d /proc/"$ALARM_PID" ]; then kill -9 $ALARM_PID &>/dev/null || true fi alarm "5" & ALARM_PID=$! done
when the alarm runs, the script executes a user-defined command that is supposed to make the daemon reload its configuration. In this example the command is kill -s HUP `pidof freeradius` and is meant to signal FreeRADIUS to reload its configuration by delivering a HUP signal. Both the directory to be watched and the reload command can be modified and adjusted to match whatever other daemon must be monitored for configuration changes.
Enumerate Services that Have not Been Replicated Completely Within a Docker Swarm
The following script can be used in order to list the services in a Docker swarm that have not fully replicated within the swarm. The script will output just the name of the services that have not been fully replicated. In order to use the script, download the text and save it to a file and make it executable.
#!/usr/bin/env bash ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2024 - License: MIT ## ########################################################################### # This script is meant to enumerate Docker swarm service names that have # # not yet replicated across the swarm. The script compares the number of # # replicas that have been distributed across the swarm with the number of # # total expected replicas and prints the service name in case there is a # # mismatch between the two. # ########################################################################### for DATA in \ `docker service ls --format="{{.Name}},{{.Replicas}}" | \ perl -pe 's/\(.+?\)//g'`; do NAME=$(printf $DATA | awk -F',' '{ print $1 }') RATIO=$(printf $DATA | awk -F',' '{ print $2 }') A=$(printf $RATIO | awk -F'/' '{ print $1 }') B=$(printf $RATIO | awk -F'/' '{ print $2 }') # If the number of replicas is equal to the number of expected # replicas then assume that the service has been already properly # distributed across the swarm. if [ "$A" = "$B" ]; then continue fi echo $SERVICE done
Computing the Total Amount of CPU Usage For All Running Containers
The following command lists the services running on a Docker node and sums up the CPU usage for all services.
docker stats --no-stream | tail -n +2 | awk '{ s+=$3 } END { printf "%.0f\n", s }'
Ensuring the Uniform Usage of CPU Resources in a Docker Swarm
One of the problems with Docker swarm orchestration is that Docker does not perform any real-time accounting of resource consumption for the services that run in the Docker swarm. Hence, once services are distributed across the swarm, it might just happen that some services start to consume resources on a Docker node unevenly compared to other nodes in the swarm. For that purpose, it makes sense to devise a script that could handle the distribution of services in order to ensure that all nodes in a Docker swarm are used evenly.
One-Shot
The following script can be ran every minute on every node of a Docker swarm in order to terminate containers after the sum total of all CPU usages of every service on the node exceeds a defined threshold. That is, in case the total CPU usage of all Docker services on a node exceeds MAXIMUM_CPU_USAGE, then the script will pick the first most CPU consuming container and will terminate that container.
#!/usr/bin/env bash ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2024 - License: MIT ## ########################################################################### # This script is meant to run on every node of a Docker swarm in order to # # terminate swarm services that consume too much CPU over a certain limit # # that can be specified by modifying the "MAXIMUM_CPU_USAGE" variable. # # # # Ideally, this script will run with crontab every minute in order to # # check whether Docker consumes more CPU than the specified limit. On # # Debian systems this can be accomplished by creating /etc/cron.minutely # # and then referencing the directory from /etc/crontab using the line: # # # # * * * * * root cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.minutely # # # # Note that after the line is added, cron must be made to reload the # # crontab, either by restarting cron or by delivering a HUP signal. # ########################################################################### MAXIMUM_CPU_USAGE=70 [ $(docker stats --no-stream | tail -n +2 | awk '{s+=$3} END {printf "%.0f\n", s}') -gt $MAXIMUM_CPU_USAGE ] && \ docker stats --no-stream | tail -n +2 | awk '{ print $1,$3 }' | sed 's/%//g' | sort -k2,2n | tail -n 1 | awk '{ print $1 }' | xargs docker stop
It is assumed that after terminating the container, the node manager will redistribute the service in the swarm, and hopefully the service will run on a node with a smaller workload.
This method does not require knowledge of other nodes.
Sampling
This variation is somewhat better because if the one-shot script just happens to be scheduled concomitantly with the start of a CPU-intensive service, the one-shot script will consider that the resources are being misused and will more than likely stop the CPU-intensive service before it boots up completely. Naturally, it is assumed that after a service starts completely, the software will stop being CPU intensive and typical of all software, will end up in an idle state.
With that being said, the following script follows the one-shot termination script from the previous section, but additionally samples the CPU usage of all services over time in order to make sure that the CPU consumption has been overstepped over a period of time before the script starts terminating containers.
#!/usr/bin/env bash ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2024 - License: MIT ## ########################################################################### # This script is meant to measure and detect CPU overload on a Docker # # swarm node and then begin to stop containers with the hopes that the # # containers will be restarted and distributed to different nodes in the # # Docker swarm. # # # # This script should be called periodically at a time interval t and each # # time the script is called a total service CPU measurement m is taken # # and deposited into a file under /dev/shm/ (to not burn flash memory). # # That being said, the script will begin stopping services iff.: # # # # ( m(t_{1}) + ... + m(t_{SAMPLE_TICKS}) ) / SAMPLE_TICKS > THRESHOLD # # # # where both SAMPLE_TICKS and THRESHOLD can be changed by the user. # # # # It is up to the user to find a way to run this script periodically, and # # one possibility is to run this script every minute using cron. Note # # that the script is meant to collect SAMPLE_TICKS samples, such that # # running this script on a more than hourly basis will make this script # # have little effect in sampling the actual CPU consumption of services. # ########################################################################### ########################################################################### # CONFIGURATION # ########################################################################### # the sum total CPU consumption that all services on a node must exceed # in order to being stopping containers and hopefully migrating services CPU_THRESHOLD=90 # this program is meant to kill processes due to the sum total of all # docker containers imposing an overload on the current node that the # program operates on but a few processes (up to 2 or 3) that temporarily # execute above the CPU threshold do not represent the sum total of all # delegated Docker processes to this node and no actions should be taken # # larger values will make this program more eager to terminate stray # single processes that are overloading the machine DEVIATION_THRESHOLD=5 # the amount of samples to collect over time SAMPLE_TICKS=5 ########################################################################### # INTERNALS # ########################################################################### # Acquire a lock. LOCK_FILE='/var/lock/docker-ooc-killer' if mkdir $LOCK_FILE 2>&1 >/dev/null; then trap '{ rm -rf $LOCK_FILE; }' KILL QUIT TERM EXIT INT HUP else exit 0 fi if [[ ! -f /dev/shm/docker-ooc-killer ]] || \ [[ $(wc -l /dev/shm/docker-ooc-killer | awk '{ print $1 }') -lt $SAMPLE_TICKS ]]; then docker stats --no-stream | \ tail -n +2 | \ awk '{ s+=$3 } END { printf "%.0f\n", s }' >> /dev/shm/docker-ooc-killer exit 0 fi # compute the total average usage across the last sample minutes echo "Computing total load across timespan." AVERAGE_USAGE=$(($(cat /dev/shm/docker-ooc-killer | awk '{ s+=$1 } END { printf "%.0f\n", s }')/$SAMPLE_TICKS)) if [ $AVERAGE_USAGE -gt $CPU_THRESHOLD ]; then # compute the standard deviation echo "Computing standard deviation..." SD=$(docker stats --no-stream | \ tail -n +2 | \ awk '{ print $3 }' | \ tr -d "%" | \ awk '{ x += $0; y += $0 ^ 2 } END { print int(sqrt( y/NR - (x/NR) ^ 2)) }') [ $SD > $DEVIATION_THRESHOLD ] && echo "Pass on high deviation. Looping." && break echo "Node is too overloaded, terminating top process." docker stats --no-stream | \ tail -n +2 | \ awk '{ print $1, $3 }' | \ sed 's/%//g' | \ sort -k2,2n | \ tail -n 1 | \ awk '{ print $1 }' | \ xargs docker stop fi rm /dev/shm/docker-ooc-killer
The script additionally computes the standard deviation in case it notices that the CPU threshold has been exceeded in order to determine whether the node is overloaded due to one or two or a few containers or whether simply too many containers have been delegated to the current node. The idea is if just one or two or a few singular processes increase the overall CPU usage footprint, then no action should be taken because the CPU threshold does not reflect the overall usage of all Docker containers.
Maybe one two or a few processes just got a task to execute or perhaps the container is just spooling up with the program inside trying to reach its idle loop, etc., in which case you definitely do not want to terminate any processes. The script should only act when some derived perception of "all containers overloading the current node" is determined, not to terminate processes that are just temporarily CPU spiking.
This method does not require knowledge of other nodes.
Ensuring Correct Replica Numbers for Services in a Swarm
Sometimes Docker ends up starting more replicas of a service than defined, or, due to nodes going up or down, Docker sometimes ends up with excess replicas of services. From time to time, it would be useful to ensure that these services are correctly re-balanced in order to correspond to their requested number of replicas. To find out the ratio of stated replicas per requested replicas, the command:
docker service ls
would list services that have a ratio exceeding 1, for example, in the event that the previous command would output services like:
... ... replicated 5/4 ... ... ... ... ... replicated 2/1 ... ... ... ...
In order to fix that, a solution is to periodically scan running services and run a script that would detect the excess replicas and restart the service to hopefully ensure that they get properly redistributed. The following script accomplishes that task by checking if the number of replicas is larger than the number of requested replicas per services and then if the check holds true, try to forcibly update the service (which, as deep magic, figures as a service restart).
#!/usr/bin/env bash ########################################################################### ## Copyright (C) Wizardry and Steamworks 2025 - License: MIT ## ########################################################################### docker service ls --format="{{.ID}} {{.Replicas}}" | \ awk -F' |\/' '{ if ($2 > $3) print $1 }' | \ xargs -I{} docker service update --detach=false --force {}
It is recommended to drop this into some crontab folder like /etc/cron.hourly.
Making inotify available in Docker Containers on NFS Mounts
Programs that require inotify will not run properly within containers that use NFS to mount drives remotely but there is a workaround possible to make inotify filesystem notifications available to Docker containers by mounting the NFS filesystem on the host and then use a bind-mount to map the directory into the container.
In other words, instead of mounting the NFS filesystem using Docker, for example via:
version: "3.9"
services:
...
volumes:
- myapp:/home/node/app
volumes:
myapp:
driver: local
driver_opts:
type: nfs
o: addr=192.168.1.1,rw,vers=4.1
device: ":/path/to/dir"
simply mount the NFS filesystem on the host by using fstab and then bind-mount the filesystem into the container:
version: "3.9"
services:
...
volumes:
- /mnt/app/data:/home/node/app
where /mnt/app/data is an NFS mounted filesystem.
Now, within the container, the path /mnt/app/data/ will have filesystem inotify notifications enabled.
Running Replicas on All Nodes
In order to run a precise number of replicas the replicas key can be used within the deploy section. For example, the following configuration:
deploy: replicas: 2
will run two replicas in a Docker swarm.
However, the question is how to run as many replicas as there are nodes but in a way that will allow scaling up the swarm and the service would seamlessly scale up without amendments. The answer is to use mode and set it to global within the deploy section as well, as in:
deploy: mode: global
which will ensure that as many replicas as there are nodes will be run.
Transfer Docker Images Between Machines
Due to images being large, public repositories implement throttling and limitations in order to not exhaust their bandwidth, especially given repetitive calls which makes it necessary to be able to transfer images between machines sometimes when the limits have been exceeded.
For that purpose, in order to export an image to a file, issue:
docker save -o /path/to/image/mongo.img mongo:windowsservercore
where:
/path/to/image/mongo.imgis the path to a file into which the image will be stored,mongo:windowsservercoreis the image to save to the file
respectively, in order to import the image on the destination machine:
docker load -i /path/to/image/mongo.img
where:
/path/to/image/mongo.imgis the path to the image file saved
Gracefully Terminating Containers
It is common to terminate containers using the parameters rm -f given that the idiom is similar to the delete command used all the time under *nix OSes but rm is meant to remove a container forcible and not wait for its termination. Graceful termination in Docker terms, means that Docker will deliver a SIGTERM (the default) signal to the entry point running inside the container and then will await for  (the default) before finally terminating the container. The signal and the timeout period can be customized depending on the environment.
(the default) before finally terminating the container. The signal and the timeout period can be customized depending on the environment.
Command-Line
On the command line, the stop sub-command has to be used:
docker stop CONTAINER
where:
CONTAINERis a container ID
to ensure that Docker will await for a graceful termination of the container.
Containers can be launched on the command line by additionally passing the --stop-timeout n parameter as well as --stop-signal SIGNAL where n is a number of seconds, respectively SIGNAL is a signal name, such that the docker stop CONTAINER where CONTAINER is the container ID will deliver the SIGNAL and then await n seconds before forcibly removing the container.
Compose
Graceful termination can be specified within a compose file, using the service-level parameters stop_signal and stop_grace_period, as in:
services:
...
NAME:
...
stop_signal: SIGHUP
stop_grace_period: 60s
Swarm
There is no "explicit" graceful termination with a Docker swarm but the same effect is achieved by scaling down a service to zero:
docker service scale SERVICE_NAME=0
where:
SERVICE_NAMEis the name of a service
After that, the rm command can be used as usual:
docker service rm SERVICE_NAME
because the scaling just achieves the effect of not running any replicas within a swarm such that the service will sit there with a zero-count for the replicas but it will not be removed from the list of running services (even if nothing is running).
It is probably best to create easy-to-type macros in order to deliver the two commands dependent upon each other in order to gracefully terminate swarm services.
Compose: Run Multiple Commands on Startup
Sometimes it so happens that some commands must be ran before running the main service within a container such that a way must exist to specify multiple commands within the same compose file. Perhaps the easiest is to do it the following way:
version: '3.8' services: rtorrent: image: rtorrent entrypoint: ["/bin/sh","-c"] command: - | rm -rf /config/rtorrent.lock rtorrent -n -b 0.0.0.0 -d /downloads -o session.path.set=/config,system.daemon.set=true
As can be observed, the entrypoint is redefined by the compose file to just run the shell with the command parameter and then the command line overrides the commands to run on startup. Furthermore, the command line allows multiline commands in the compose file by using the - | operator.
The Argument Against Process Management within Containers
One of the frequent patterns that wildly in use is to use a process manager, typically supervisord, but also others like monit or s9 to ensure that processes within the container are kept alive.
Others critique the pattern by stating that containers and containerization is meant for a single "application" but what thy miss is that the semantics of "application" refers to an "usage pattern" not "software". In other words, containerization is supposed to wrap an "application" such as "the automatic updating of a website", which does not exclude running multiple program, software or other tools in order to achieve the goals of the "application".
On the other hand, the usage pattern of "process managers" within containers implies the restart of long-running services within a container, which, unfortunately, breaks the usage pattern of containers because once a "long-running process" meant for an "application" has failed (in other words, one of the components of the application, abstractly speaking) then the container should be marked as unhealthy and the whole container is meant to terminate.
With that being said, and for people that find it more "elegant" to run a process manager, seeking an alternative to process managers, such efforts are not only wasted but also violate the intended usage of the technology. Of course, since starting multiple processes is still in-line with using a single container per application, some alternative must be found. Ideally, only one single software package must be run, in which case the ENTRYPOINT can be set directly to run the process and when the process terminates, then the container terminates with it, which is perfect. However, when multiple programs have to be started, monitoring all of them (as components) is necessary in order to stop the container.
The following script is built into the container and then it is set as the ENTRYPOINT for the container:
#!/bin/bash echo "Starting..." sleep 1000000 & sleep 1000000 & # terminate container when any process spawned by this shell in the background terminates for JOB in `jobs -p`; do (lsof -p $JOB +r 1 &>/dev/null; kill -s TERM 1) & done sleep infinity
In brief, the script writes "Starting..." to the standard output, spawns two processes sleep and then backgrounds the processes, goes through the list of process identifiers (PID) for all long-running processes started by the current script and spawns a smaller program for each PID that is placed in the background.
The smaller snippet runs in the background for each long-running process:
(tail --pid=$JOB -f /dev/null; kill -s TERM 1) &
and it uses tail to block execution until the PID of the long-running process contained inside the loop variable $JOB expires (ie: the process terminates) and then delivers a kill signal to the container itself via kill -s TERM 1 (which kills the Linux entry point, init, which, in turn, will terminate the container altogether).
Here are some remarks:
- The small snippet inside the loop is backgrounder using the ampersand operator, which is necessary to satisfy the "any" clause of the requirement, because it is necessary to terminate the container when any (not all) process in the background fails. If it would be required to wait for "all" processes to terminate, then the whole loop could just be substituted with a single
waitcommand. lsofitself is not necessarily portable, but this command can be replaced with any equivalent that blocks while the PID exists in order to runkillright after that.- If
exitwould have been used, the container would have not terminated due the theexitcommand existing within the subshell context before the ampersand, which would have made the subprocess that waits on the PID terminate, which is trivial and would not even warrant anexitin the first place. - The first
echocommand is not captured byjobs -p, which is great, because theechocommand would have terminated by the timejobs -pis ran such thatjobs -ponly accounts for processes spawned by this shell that are still running (in the background). - When the script is made the
ENTRYPOINTof the container, then the script is, in fact, theinitprocess, which is equivalent to PID1such thatkill -s TERM 1terminates the script itself. Conventionally the PID of the current script is lifted from$$within Bash, but since Linux is running and the script is theENTRYPOINT, thenkill -s TERM 1has the exact same effect as storing and killing$$because$$contains1in this usage pattern.
Jumbo Frames and Docker Swarm
Please be aware that jumbo frames seem to produce hard-to-track issues even if properly configured. When in doubt, just run the network adaptor with jumbo frames but leave the Docker or Docker Swarm stack alone to use the standard MTU.
Go Templating inside Docker Compose for Docker Swarms
Docker Compose supports Go templating such that it is possible to conditionally configure a service with parameters from the local node that it is started from. For example, the service file:
version: '3.8'
services:
cronicle:
image: cronicle:latest
hostname: "{{.Node.Hostname}}"
...
will create a service named cronicle and depending on which node the service is started, the hostname will be set to the hostname of the local node.
System-Wide Registry Authentication
docker will store registry credentials in the home-folder of the user that is logging in to registries which can be a bit of a bother on non-multiuser systems or in situations where a system administrator would like to offer accounts to an entire infrastructure.
In order to create system-wide credential file that will be used by all users using docker, the credentials file that is generated using docker login to be found at ~/.docker/config.json can be moved to /etc/docker/ and a global environment variable named DOCKER_CONFIG should be set that points to the /etc/docker directory.
Now, when a user attempts to access a registry, docker will read /etc/docker/config.json and authenticate as necessary.
Attach Container to Real Network
For some purposes such as services that rely on network-wide broadcasting like mDNS, it is a requirement that the container be connected to the real network such that it can reach real machines directly. In order to accomplish that, Docker provides a macvlan networking mode where the container is attached like a bridge to a physical network interface.
To set up macvlan in order to give a container direct access to the network, first create a macvlan network:
docker network create \
-d macvlan \
--subnet 192.168.1.0/24 \
--gateway 192.16.1.1 \
-o parent=eth0 \
docker_macvlan
where:
192.168.1.0/24is the real network,192.168.1.1is the real network gateway,eth0is the real network interface to attach the container to and,docker_macvlanis a descriptive name for the network being created
Conversely, in order to make a container attach to the newly created docker_macvlan network, issue:
docker run -it \ --net=docker_macvlan \ --hostname debug \ --name debug \ --ip=192.168.1.50 \ --interactive \ --entrypoint /bin/bash \ jonlabelle/network-tools
and the command will download the jonlabelle/network-tools container and spawn a shell inside it, where:
docker_macvlanis the descriptive name of the macvlan network created previously,172.16.1.27is a free IP address on the network
Now, from within the container, it is possible to reach the rest of the network and the connection should work back and forth via the IP address.
Cleaning up Registry
Up to v2, the Docker registry would just store images but there would be no way to delete the images nor was there any possibility of cleaning up older or untagged images. With v2 onward, the situation changes and the Docker registry can be configured to clean up images. In order to periodically clean up older or untagged images, the following steps can be followed.
First, the following Docker compose registry service file defines the REGISTRY_STORAGE_DELETE_ENABLED environment variable that will make registry allow deleting image files:
version: '3.8' services: registry: image: registry:latest ports: - 5000:5000 environment: - REGISTRY_STORAGE_DELETE_ENABLED=true volumes: - /mnt/local/registry/auth:/auth - /mnt/local/registry/registry-data:/registry-data - /mnt/local/registry/config.yml:/etc/distribution/config.yml deploy: labels: - shepherd.enable=true - shepherd.auth.config=docker replicas: 1 placement: max_replicas_per_node: 1
with the local file /mnt/local/registry/config.yml mapped to /etc/distribution/config.yml within the container, containing a sample configuration along the lines of:
version: 0.1 log: fields: service: registry storage: cache: blobdescriptor: inmemory filesystem: rootdirectory: /registry-data tag: concurrencylimit: 8 http: addr: :5000 headers: X-Content-Type-Options: [nosniff] auth: htpasswd: realm: Registry path: /auth/registry.password health: storagedriver: enabled: true interval: 10s threshold: 3
where:
/auth/registry.passwordis a HTTP user and password pair generated with thehtpasswdcommand-line utility
The next step is to follow the instructions of registry-cli maybe even by installing the utility as a docker container.
Now, periodically, while registry runs in the background, the following command can be ran in order to mark images for deletion:
docker run \ --rm anoxis/registry-cli \ -l USERNAME:PASSWORD \ -r http://REGISTRY_HOST:REGISTRY_PORT \ --delete
where:
USERNAME:PASSWORDis the authentication tuple for the registry generated withhtpasswdand referenced in the registry configuration file/mnt/local/registry/config.yml,http://REGISTRY_HOST:REGISTRY_PORTis the URL to the registry to clean up
The command will keep the last 10 variants of the same image and mark the rest for deletion.
With the images marked for deletion, the garbage-collect command within the registry image container must be triggered in order to actually remove the images. Here is an example invocation:
docker exec REGISTRY_CONTAINER_ID \ registry garbage-collect /etc/distribution/config.yml --delete-untagged=true
where:
REGISTRY_CONTAINER_IDis the container id of the currently running registry image, obtained, for example, by runningdocker container lsand,/etc/distribution/config.ymlis the Docker registry configuration file within the container referenced in the Docker compose file from earlier
After running the last command, the older images and untagged images will be finally removed.
Doing this manually every time would be a pain so a much easier way would be to automate the process, for example by creating a script to be ran with cron. The following is a rough draft:
docker run \ --rm anoxis/registry-cli \ -l USERNAME:PASSWORD\ -r http://REGISTRY_HOSTNAME:REGISTRY_PORT \ --delete docker container ls --format "{{.Names}} {{.ID}}" | \ grep ^registry | \ awk '{ print $2 }' | \ xargs -I'{}' \ docker exec '{}' registry garbage-collect /etc/distribution/config.yml --delete-untagged=true
The first command will flag the images for deletion and the next command fetches all the containers, determines the ID of the container running "registry" and then runs a command within the "registry" container to garbage collect the images marked for deletion as well as delete all untagged images.
Referring to Other Containers within a Swarm
As long as all containers are part of a network overlay, just like in a swarm, it is possible to refer to a container by using the service name as the host name, at which point Docker will resolve the service name to the IP address of the container on the same overlay network. Note that regarding ports, whatever service is running, will have to be accessed via its internal port and not its outbound mapped port when referring to a different container from within another containers.
Deleting Images from Docker Registry using the REST API
Given a registry set up following the registry instructions to enable deletions, it is possible to delete individual images.
The first step is to list the existing images:
curl -u "USERNAME:PASSWORD" -s "REPOSITORY_HOSTNAME:REPOSITORY_PORT/v2/_catalog"
where:
USERNAMEandPASSWORDare the registry credentials,REPOSITORY_HOSTNAME:REPOSITORY_PORTrepresent the hostname and port pair used to access the Docker registry
Then, the tags for the image are listed with:
curl -u "USERNAME:PASSWORD" -s "REPOSITORY_HOSTNAME:REPOSITORY_PORT/v2/top/tags/list"
which should yield a list of tags for the image like version numbers or the usual latest for the latest image. Assuming the images in the latest tag are supposed to be deleted, issue:
curl -s \ -u "USERNAME:PASSWORD" \ -H 'Accept: application/vnd.docker.distribution.manifest.v2+json' \ -w '%header{Docker-Content-Digest}' \ -o /dev/null \ 'REPOSITORY_HOSTNAME:REPOSITORY_PORT/v2/top/manifests/latest'
which should yield a long hash alogn the lines of sha256:... which can then be used to delete the image.
curl -s -u "USERNAME:PASSWORD" -X DELETE 'REPOSITORY_HOSTNAME:REPOSITORY_PORT/v2/top/manifests/HASH'
where:
HASHis the manifest hash
Note that, the image will be marked for deletion but will not effectively be deleted such that registry must be told to run the garbage collector.
For Deleting Images Identical Hashes
One of the problems that was encountered when building an image was that issuing docker push would not update the existing image in the registry because Docker considered that the image that already existed because it had the same hash as the image that was currently built. Tracing the problem, it was noticed that the only change made within the image was naming a binary differently, yet the binary itself did not change in any way, such that the hashes between the image stored in the registry and the new image that was build were identical because Docker does not consider the actual file names when generating the hash. This had the effect that the old image was being run when a container was started which felt exasperating because the contents of the container did not match the contents of the image that was just built.
Intuitively, Docker hashes the image by its contents in terms of binary length but the files can be moved around because it will not make a difference for the generated hash. With that being said, deleting images is most useful for these cases where the container would have to be changed a little in terms of contents for the hash to be updated.
Using tmpfs with Docker Swarm via Compose
tmpfs volumes can, in fact, be used with Docker swarm. It is just that the volume must be declared separately, as in:
version: '3.9' services: myservice: image: ... read_only: true volumes: - tmp:/var/run volumes: tmp: driver_opts: type: tmpfs device: tmpfs o: "size=1m,noexec,nosuid,nodev"
where tmp is a volume name created in RAM.
GLibc Binaries on Alpine Linux
Alpine Linux is the preferred dockerization Linux distribution and operating system for Docker builds due to Alpine being an effort to create a minimalist Linux distribution which, when used as the base image for Docker makes the resulting built images be very small in terms of size which is a property that is relevant for Docker users.
One of the most common errors is illustrated by the following example where Corrade is ran under Alpine Linux:
grimore_corrade.1.yem8cjw15arh@docker1 | /usr/local/bin/run: line 23: /corrade/Corrade: cannot execute: required file not found
which implies that when the binary /corrade/Corrade binary is ran from the shell script /usr/local/bin/run, the error cannot execute: required file not found is thrown and the software does not start.
The error "cannot execute: required file not found" is an indication that no glibc compatibility has been installed when the image has been built. In order to make sure, ldd can be used to check the dynamic link-library tree for a binary that is not entirely static - in our case, the Wizardry and Steamworks Corrade software is not entirely built statically, but rather "self-contained" and with some very minimal requirements such that there are still some dynamic libraries that the executable needs. Using the "ldd" tool, and running from the script:
ldd /corrade/Corrade
results in the following list of requirements:
grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x7f95ddd07000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | libdl.so.2 => /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x7f95ddd07000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | librt.so.1 => /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x7f95ddd07000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | libgcc_s.so.1 => /usr/lib/libgcc_s.so.1 (0x7f95dd130000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x7f95ddd07000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | libstdc++.so.6 => /usr/lib/libstdc++.so.6 (0x7f95dce7e000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | libm.so.6 => /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x7f95ddd07000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | libc.so.6 => /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x7f95ddd07000) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | Error loading shared library ld-linux-x86-64.so.2: No such file or directory (needed by /corrade/Corrade) grimore_corrade.1.w9z8tqbx5d21@docker2 | Error relocating /corrade/Corrade: __strdup: symbol not found
It's in fact a funny error, namely the Corrade software is missing a function strdup that is usually contained within the glibc library ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 and the function is actually a low-level C function that duplicates a string or rather an array of characters using low-level terminology.
The fix is to amend the Dockerfile and add some glibc support, first by trying to install a (minimal) glibc compatibility layer:
RUN apk add --no-cache bash unzip curl icu gcompat
where:
gcompatis the minimal glibc compatibility library
It is also possible to install the full glibc library on Alpine, but it's going to waste a lot of space:
# Source: https://github.com/anapsix/docker-alpine-java
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/66963068/docker-alpine-executable-binary-not-found-even-if-in-path
ENV GLIBC_REPO=https://github.com/sgerrand/alpine-pkg-glibc
ENV GLIBC_VERSION=2.30-r0
RUN set -ex && \
apk --update add libstdc++ curl ca-certificates && \
for pkg in glibc-${GLIBC_VERSION} glibc-bin-${GLIBC_VERSION}; \
do curl -sSL ${GLIBC_REPO}/releases/download/${GLIBC_VERSION}/${pkg}.apk -o /tmp/${pkg}.apk; done && \
apk add --allow-untrusted /tmp/*.apk && \
rm -v /tmp/*.apk && \
/usr/glibc-compat/sbin/ldconfig /lib /usr/glibc-compat/lib
Relocating Storage
Docker has some considerable space requirements, in particular, if images are being constantly swapped out or built. Most of the storage used is mostly ephemeral and could be flushed typically after a container terminates. Unfortunately, given a standard install, Docker and containerd place all images and runtime artefacts on the root partition within /var/lib.
We have written up some thoughts on contextualizing storage space which would hint that the usage pattern of Docker does not match the general usage pattern of a Linux system such that the Docker-related files could be moved to a different storage medium.
Relocating Docker Data
This is the typical folder that needs to be cleaned with docker system prune -a -f --volumes or it gets too large over time given that every image is stored by a hash such that all older versions exist.
In order to relocate this folder somewhere else, say /mnt/docker/runtime, a copy of /lib/systemd/system/docker.service should be made to /etc/systemd/system/docker.service and then edited to specify the different path. Specifically, the arguments to dockerd should be changed to include the --data-root parameter along with a chosen path:
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --data-root /mnt/docker/runtime/ --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
where:
--data-rootis the newly added parameter
Relocating Containerd
Containerd is modernly used as the backing store for Docker in order to store containers and it can get bloated as well, such that relocating it might be a good idea.
In order to do so, change /etc/containerd/config.toml in order to set a new root. For example, the setting:
root = "/mnt/docker/runtimes/containerd"
will place all container artifacts under /mnt/docker/runtimes/containerd.
Avoiding Excess Session-File Accumulation when Running a LAMP-Like Stack Under Docker
PHP tends to create server-side session files for connecting clients, mostly used to track clients and settings that they might make on a given page. The session is created by PHP itself and stored in the path specified by the setting session.save_path in php.ini, by default that would be /var/lib/php/sessions.
Typically PHP is meant to probabilistically run a thread in order to clear up the session files from the session path specified in the configuration but on Debian there is a note placed by default in php.ini that states that session file cleanup is disabled on Debian and offloaded to cron.
Indeed, there is a file created at /etc/cron.d/php that calls the necessary scripts to clean up the session directory. However, iff. the Docker container was created without the "cron" software package, and by default there is no dependency between "cron" and the PHP packages, then the /etc/cron.d/php script will not run.
As a simple solution, always remember to include cron when creating a LAMP-like stack because it might be needed by software like PHP. A bug report has been filed with Debian package maintainers.
Using Docker for Builds within Reproducible Environments
Compiling packages on a system often incurs a local penalty where some dependencies might be created to some assets to be found on the current operating system such that when a bug is reported, the developers are unable to observe the bug.
One of the good uses of Docker is to create build environments that have the property that they can be easily reproduced for the purpose of testing and checking for bugs.
For example, the following Dockerfile sets up an environment based on an untouched Debian stable distribution and preloads just a few utilities and settings that are necessary in order to bootstrap a compilation:
FROM debian:stable
# use the current debian stable distribution
# update package manager
RUN apt-get update -y && \
apt-get upgrade -y && \
apt-get dist-upgrade -y && \
apt-get -y autoremove && \
apt-get clean
# UTF-8 support
RUN apt-get install -y coreutils locales && \
sed -i -e 's/# en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8/' /etc/locale.gen && \
locale-gen && \
dpkg-reconfigure --frontend=noninteractive locales && \
update-locale LANG=en_US.UTF-8
# set environment variables
ENV LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
ENV LANG=en_US.UTF-8
ENV LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8
# install required packages
RUN apt-get install -y \
sudo \
build-essential \
git
RUN useradd -rm -d /home/debian -s /bin/bash -g root -G sudo -u 1000 debian
RUN echo "debian ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL" > /etc/sudoers.d/10-debian
USER debian
WORKDIR /home/debian
ENV HOME /home/debian
ENV DISTRO debian
VOLUME /home/debian
CMD bash
The contents are saved to a file named Dockerfile that is ideally placed in the parent directory containing the source of the program to compile and then the following commands are ran, first to build the environment and name it environment-debian:
docker build -t environment-debian .
after which the environment is started and the terminal is switched inside the container by issuing:
docker run --rm -it -v $(pwd):/home/debian debian
Now, within the container it is possible to download the software and attempt to compile it. Any other user that would like to reproduce the compilation, would easily be able to by building the very same Dockerfile which would lead to the very same environment (ideally, the stable tag for the Debian distribution would be replaced by a distribution release codename).
Starting and stopping containers for this purpose is fairly efficient and also very clean for the Docker host because the contents of the container will be discarded once the container is stopped (ie: the user exited the shell). This ensures that the host does not become polluted with various trash and hacks that were necessary to compile a software package.