Vernam Cypher
The Vernam cypher is a one-time pad cypher where the encryption key is chosen to be of the same size as the plain-text to encrypt. There are several takes on the one-time pad encryption, but generally the encryption is symmetric to its decryption and consists in combining the plain-text with the key-text letter-by letter.
Supposing that the index of the plain-text letter is 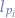 and that the index of the key-text letter is
and that the index of the key-text letter is 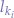 , we obtain the cypher-text letter
, we obtain the cypher-text letter 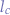 through:
through:
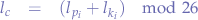
In order to reverse the cypher, the verse operation is performed:
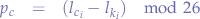
The operation used for encryption (in this case addition) has to have an inverse operation (in this case subtraction) in order to be able to decrypt.