Table of Contents
Enable Developer Options
There are several ways to do this depending on the device, but usually the procedure is to open the Android settings application and find something along the lines of About or About phone. Enter the menu selection and you should get various information on your device. Scroll all the way down and find the item Build number and tap it 10 times - after 5 taps the device will tell you that you are 5 taps away from becoming a developer.
Access Android via The Command Line
First, developer mode has to be enabled and Settings->Developer options->USB Debugging has to be enabled. Instead of installing an SSH server to be able to log-in to a rooted Android device, the adb tool can be used instead.
On OSX, adb can be installed via Homebrew:
brew install caskroom/cask/android-platform-tools
Once the device is connected via USB, issue:
adb shell
You may get the error message:
error: device unauthorized. This adb server's $ADB_VENDOR_KEYS is not set Try 'adb kill-server' if that seems wrong.
in which case, issue adb shell again but pay attention to the Android device screen because Android will prompt for authorization.
Write to Root Filesystem
In order to be able to write to the root filesystem, issue:
mount -o remount,rw /
Some folders in the root are symlinked into the /system/ filesystem, which can also be (re)mounted with read-write permissions instead of read only:
mount -o remount,rw /system
Generating Keys and Signing Packages
Keys can be generated by issuing:
openssl genrsa -out key.pem 1024 openssl req -new -key key.pem -out request.pem openssl x509 -req -days 9999 -in request.pem -signkey key.pem -out certificate.pem openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -outform DER -in key.pem -inform PEM -out key.pk8 -nocrypt
and then can be signed using aospsign.jar (also available from Google):
java -jar SignApk.jar certificate.pem key.pk8 Application.apk Application_signed.apk
where:
Application.apkis the application to sign,Application_signed.apkis the resulting file
A package can be opened with a simple zip program and you do not need to use apktool if you are looking to reverse-engineering Android packages.
Disable Hardware Keys
To disable hardware keys, root is needed and then a hardware key map file must be edited. Using a root explorer, navigate to /system/usr/keylayout and locate the keylayout file - Generic.kl should work for most devices, mtk-kpd.kl works for MediaTek devices (AllView).
Edit the file and place a hash sign (#) in front of the button mapping, for instance:
key 115 VOLUME_UP
will turn into:
#key 115 VOLUME_UP
Finally, restart the device for the changes to take effect. Note that this is a good and reliable way to disable the power button.
Completely Disable Calls
An easy trick to disable calls (such as the emergency call button from the lock screen), is to go to the phone settings, manage applications and disable the Dialer or Phone application.
Android x86 on LibVirt
In case Android x86 under qemu/kvm boots to a command prompt (or just displays a blank screen with a curor) and does not go any further then most likely the problem is that -vga std has to be passed to the qemu/kvm command line.
After installing Android under libvirt, the domain name has to be edited, for instance:
virsh -c qemu:///system
followed by:
edit android.domain
The video tag has to be deleted and replaced by:
<video>
<model type='vga'/>
</video>
to allow Android to boot the window manager.
Even better:
<video>
<model type='virtio'/>
</video>
can be used for 3D acceleration.
Delivering Input Events via ADB
Input events can be sent to a device connected to a computer with the Android Platform Tools installed via the adb command.
Here is a list of useful commands:
adb shell input tap 500 600
will tap the screen at 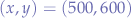 .
.
adb shell input text 'Hello Android'
will type in the text 'Hello Android'.
Even raw key events can be sent:
adb shell input keyevent 66
will press the enter key.
Similarly, D-PAD events can be triggered:
| Direction | KeyCode |
|---|---|
| Up | 19 |
| Down | 20 |
| Left | 21 |
| Right | 22 |
For instance:
adb shell input keyevent 19
will press D-PAD up.
Fixing MicroG/UnifiedNLP Permissions
Issue the following commands via ADB to fix permissions for most packages involved with UnifiedNLP:
pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant org.microg.nlp.backend.ichnaea android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant org.microg.nlp.backend.ichnaea android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION pm grant org.microg.nlp.backend.ichnaea android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE pm grant org.fitchfamily.android.dejavu android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant org.fitchfamily.android.dejavu android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE pm grant com.google.android.gms android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE pm grant com.android.vending android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE pm grant org.microg.nlp.backend.ichnaea android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant org.microg.nlp.backend.ichnaea android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION pm grant org.microg.nlp.backend.ichnaea android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE pm grant org.fitchfamily.android.dejavu android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION pm grant org.fitchfamily.android.dejavu android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION
Unlock via TWRP
Delete the files under /data/system:
password.keypattern.keylocksettings.dblocksettings.db-shmlocksettings.db-wal
Hiding Root with Magisk
Here are a few measures you can take for hiding root if you are using Magisk from the Magisk settings:
- enable Zygote,
- hide the Magisk application,
- enable DenyList and enable enforcing the DenyList
Now depending on whether you are using microG services or the standard Android Google services, some applications should be blocked using the Magisk DenyList.
Intuitively, the application to hide root from should also be blocked using the Magisk DenyList feature.
Hiding Applications with Shizuku or Dhizuku even on Non-Rooted Phones
Android is a true dystopian battlefield out of 1984, with spyplications refusing to either run on rooted phones or even having a preference of what other applications are installed on the phone. Counter-intuitively, these spyplications are not your run-of-the-mill fat hackers in a hoodie living in their mom's basement but rather banking, shipping and government applications.
Revolut a large online bank, for example, has recently updated itself to not run on rooted phones. However, even if the phone is not rooted, Revolut has a list of applications that it refuses to run if they are also installed, even applications that have little to do with gaining illicit access.
For that purpose, it is sometimes necessary to hide an application from other applications. In the past, this could be accomplished with Amarock that would hide itself and also hide other applications from other applications. However, an updated procedure is to use Shizuku or Dhizuku where the former, Shizuku requires root and Dhizuku does not require root.
The instructions are paraphrased from the original author, iamr0s but just explained in more detail:
- Shizuku will have to be installed (do not worry because it will not require rooting the system) and follow the procedure to first perform the pairing, and then click the "Run" button,
- Install the Hail application that will be used to freeze and hide applications,
- Open up the Hail application, go to Settings and set the "Working mode" to "Shizuku - Disable",
- Use the AndroidAccounts application to get a list of accounts on the system, these might even turn out to be created by your bank,
- Look for the application matching the accounts reported by "AndroidAccounts" in the Hail application by going to "Apps", add them to the "Home" screen by ticking the box and click the "Freeze" button,
- Make sure you have ADB installed on a computer and then open a command prompt and type:
adb shell dpm set-device-owner --user 0 com.rosan.dhizuku/.server.DhizukuDAReceiver
- Open the Hail application again and set the "Working mode" to "Dhizuku - Hide",
- Add applications that need to be hidden from applications that do not work alongside others and click the "Freeze" button
Google Services
The following services should be blocked using the Magisk DenyList:
- Google Play Protect Services,
- Google Play Services,
- Google Play Store,
- Google Service Framework.
microG Services
microG serves the same set of functions as Google services such that all microG services have to be blocked, including:
- microG companion,
- microG Services Core,
- microG Services Framework Proxy.
Hide Folder from Gallery
In order to hide a folder from being indexed by Android, simply create an empty dotfile in the folder to be hidden named .nomedia and Android will ignore the folder from any media scanning. Note that the .nomedia dot file applies a recursive exclusion to all descendants, if any, such that the file should be created on a depth-first basis if hiding less is desired.
Allow Making Changes to Accessibility Settings for an Application
Surprisingly, the error "Restricted Setting. For your security, this setting is currently unavailable." might pop up whilst trying to enable accessibility for an application. The workaround is to go to the "App Info" section of the "Settings" application and then click the three dots in the upper right corner and select "Allow Restricted Settings". Then, going back to the accessibility settings, the option to toggle the setting for the given application should be enabled.