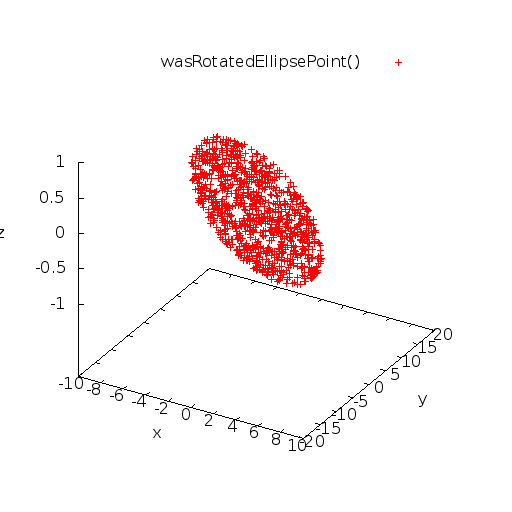
Graph
Theory
The code performs the follows the reasoning: for a chosen  and
and 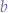 , select a random
, select a random  with
with 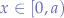 and
and 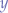 with
with 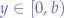 . If and only if the equation of the ellipse in standard form:
. If and only if the equation of the ellipse in standard form:
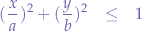
is satisfied, then the generated  and
and  values describe a point
values describe a point 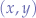 which lies within the ellipse's perimeter. Otherwise, select new values for
which lies within the ellipse's perimeter. Otherwise, select new values for  and
and  and loop until the equation is satisfied.
and loop until the equation is satisfied.
Once a point within that ellipse is generated, we rotate the point on an arc described by the specified angle  (in radians):
(in radians):
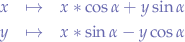
in order to obtain the rotated point.
Code
- wasRotatedEllipsePoint.lsl
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Copyright (C) 2015 Wizardry and Steamworks - License: GNU GPLv3 // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // the angle (in radians) o represents a rotation in the trigonometric // sense around the Ox axis where O represents the ellipse center vector wasRotatedEllipsePoint(float a, float b, float o) { float x = llPow(-1, 1 + (integer) llFrand(2)) * llFrand(a); float y = llPow(-1, 1 + (integer) llFrand(2)) * llFrand(b); if(llPow(x/a,2) + llPow(y/b,2) <= 1) return <x*llCos(o) + y*llSin(o), x*llSin(o) - y*llCos(o), 0>; return wasRotatedEllipsePoint(a, b, o); }